LF 16-0687 Ms, a bradykinin B2 receptor antagonist, reduces ischemic brain injury in a murine model of transient focal cerebral ischemia
- PMID: 12922942
- PMCID: PMC1573979
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705385
LF 16-0687 Ms, a bradykinin B2 receptor antagonist, reduces ischemic brain injury in a murine model of transient focal cerebral ischemia
Abstract
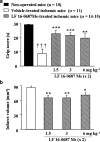
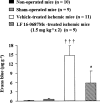
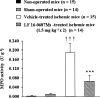
1. Bradykinin promotes neuronal damage and brain edema through the activation of the B(2) receptor. The neuroprotective effect of LF 16-0687 Ms, a B(2) receptor antagonist, has been described when given prior to induction of transient focal cerebral ischemia in rat, but there are no data regarding the consequence of a treatment when given after injury. Therefore, in a murine model of transient middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO), we evaluated the effect of LF 16-0687 Ms given prior to and/or after the onset of ischemia on neurological deficit, infarct volume and inflammatory responses including cerebral edema, blood-brain barrier (BBB) disruption and neutrophil accumulation. 2. LF 16-0687 Ms (1, 2 and 4 mg kg(-1)) administered 0.5 h before and, 1.25 and 6 h after MCAO, decreased the infarct volume by a maximum of 33% and significantly improved the neurological recovery. 3. When given at 0.25 and 6.25 h after MCAO, LF 16-0687 Ms (1.5, 3 and 6 mg kg(-1)) decreased the infarct volume by a maximum of 25% and improved the neurological score. 4. Post-treatment with LF 16-0687 Ms (1.5 mg kg(-1)) significantly decreased brain edema (-28%), BBB disruption (-60%) and neutrophil accumulation (-65%) induced by ischemia. Physiological parameters were not modified by LF 16-0687 Ms. 5. These data emphasize the role of bradykinin B(2) receptor in the development of infarct lesion, neurological deficit and inflammatory responses resulting from transient focal cerebral ischemia. Therefore, B(2) receptor antagonist might represent a new therapeutic approach in the pharmacological treatment of stroke.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Neuroprotective effects of a postischemic treatment with a bradykinin B2 receptor antagonist in a rat model of temporary focal cerebral ischemia.Brain Res. 2006 Jan 19;1069(1):227-34. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2005.11.043. Epub 2005 Dec 27. Brain Res. 2006. PMID: 16378603
-
Effects of LF 16-0687 Ms, a bradykinin B(2) receptor antagonist, on brain edema formation and tissue damage in a rat model of temporary focal cerebral ischemia.Brain Res. 2002 Sep 20;950(1-2):268-78. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(02)03053-6. Brain Res. 2002. PMID: 12231253
-
Effect of aminoguanidine on post-ischemic brain edema in transient model of focal cerebral ischemia.Brain Res. 2007 Sep 19;1170:97-102. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2007.07.016. Epub 2007 Jul 19. Brain Res. 2007. PMID: 17698046
-
Glibenclamide in cerebral ischemia and stroke.Neurocrit Care. 2014 Apr;20(2):319-33. doi: 10.1007/s12028-013-9923-1. Neurocrit Care. 2014. PMID: 24132564 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[The role of edema in cerebral ischemia. From physiopathology to therapeutics].Schweiz Arch Neurol Psychiatr (1985). 1988;139(1):17-30. Schweiz Arch Neurol Psychiatr (1985). 1988. PMID: 2451278 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Bradykinin B2 receptor antagonism: a new direction for acute stroke therapy?Br J Pharmacol. 2003 Aug;139(8):1369-71. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705415. Br J Pharmacol. 2003. PMID: 12922922 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The powerful neuroprotective action of C1-inhibitor on brain ischemia-reperfusion injury does not require C1q.Am J Pathol. 2004 May;164(5):1857-63. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63744-3. Am J Pathol. 2004. PMID: 15111332 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of carbonic anhydrase reduces brain injury after intracerebral hemorrhage.Transl Stroke Res. 2012 Mar;3(1):130-7. doi: 10.1007/s12975-011-0106-0. Transl Stroke Res. 2012. PMID: 22400066 Free PMC article.
-
Physiology of the volume-sensitive/regulatory anion channel VSOR/VRAC: part 2: its activation mechanisms and essential roles in organic signal release.J Physiol Sci. 2024 Jun 14;74(1):34. doi: 10.1186/s12576-024-00926-3. J Physiol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38877402 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of Bradykinin Postconditioning on Ischemic and Toxic Brain Damage.Neurochem Res. 2015 Aug;40(8):1728-38. doi: 10.1007/s11064-015-1675-1. Epub 2015 Jul 28. Neurochem Res. 2015. PMID: 26216051 Free PMC article.
References
-
- BARONE F.C., HILLEGASS L.M., PRICE W.J., WHITE R.F., LEE E.V., FEUERSTEIN G.Z., SARAU H.M., CLARK R.K., GRISWOLD D.E. Polymorphonuclear leukocyte infiltration into cerebral focal ischemic tissue: myeloperoxidase activity assay and histologic verification. J. Neurosci. Res. 1991;29:336–345. - PubMed
-
- BEDERSON J.B., PITTS L.H., GERMANO S.M., NISHIMURA M.C., DAVIS R.L., BARTKOWSKI H.M. Evaluation of 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride as a stain for detection and quantification of experimental cerebral infarction in rats. Stroke. 1986;17:1304–1308. - PubMed
-
- BHOOLA K., RAMSAROOP R., PLENDL J., CASSIM B., DLAMINI Z., NAICKER S. Kallikrein and kinin receptor expression in inflammation and cancer. Biol. Chem. 2001;382:77–89. - PubMed
-
- BHOOLA K.D. Translocation of the neutrophil kinin moiety and changes in the regulation of kinin receptors in inflammation. Immunopharmacology. 1996;33:247–256. - PubMed
-
- BHOOLA K.D., FIGUEROA C.D., WORTHY K. Bioregulation of kinins: kallikreins, kininogens, and kininases. Pharmacol. Rev. 1992;44:1–80. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

