Normal intestinal microbiota in the aetiopathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 12922950
- PMCID: PMC1754679
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.62.9.807
Normal intestinal microbiota in the aetiopathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
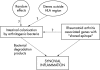
A series of observations have led to the hypothesis that normal intestinal microbiota in patients with rheumatoid arthritis may harbour, for genetic reasons, bacteria with cell walls capable of inducing arthritis. Differences occur between bacterial species, and even between strains of a single species, because some cell walls induce experimental chronic arthritis, whereas some others induce only a transient acute arthritis or no arthritis at all. In susceptible subjects, with continuous seeding of bacterial products from the gut, the synovial inflammation is followed by erosion, exposition of cartilage antigens, and self perpetuating chronic arthritis.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical