Ablate and pace revisited: long term survival and predictors of permanent atrial fibrillation
- PMID: 12923021
- PMCID: PMC1767849
- DOI: 10.1136/heart.89.9.1035
Ablate and pace revisited: long term survival and predictors of permanent atrial fibrillation
Abstract
Objective: To assess long term mortality and identify factors associated with the development of permanent atrial fibrillation after atrioventricular (AV) node ablation for drug refractory paroxysmal atrial fibrillation.
Design: Retrospective cohort study.
Setting: UK tertiary centre teaching hospital.
Patients: Patients admitted to the University Hospital Birmingham between January 1995 and December 2000.
Interventions: AV node ablation and dual chamber mode switching pacing.
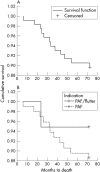
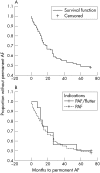
Main outcome measures: Long term mortality and predictors of permanent atrial fibrillation, assessed through Kaplan-Meier curves and logistic regression.
Results: 114 patients (1995-2000) were included: age (mean (SD)), 65 (9) years; 55 (48%) male; left atrial diameter 4 (1) cm; left ventricular end diastolic diameter 5 (1) cm; ejection fraction 54 (17)%. Indications for AV node ablation were paroxysmal atrial fibrillation in 95 (83%) and paroxysmal atrial fibrillation/flutter in 19 (17%). The survival curve showed a low overall mortality after 72 months (10.5%). Fifty two per cent of patients progressed to permanent atrial fibrillation within 72 months. There was no difference in progression to permanency between paroxysmal atrial fibrillation and paroxysmal atrial fibrillation/flutter (log rank 0.06, p = 0.8). Logistic regression did not show any association between the variables collected and the development of permanent atrial fibrillation, although age over 80 years showed a trend (p = 0.07).
Conclusions: Ablate and pace is associated with a low overall mortality. No predictors of permanent atrial fibrillation were identified, but 48% of patients were still in sinus rhythm at 72 months. These results support the use of dual chamber pacing for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation patients after ablate and pace.
Figures
References
-
- Kannel WB, Wolf PA, Benjamin EJ, et al. Prevalence, incidence, prognosis, and predisposing conditions for atrial fibrillation: population-based estimates. Am J Cardiol 1998;82:2–9N. - PubMed
-
- Moe G, Rheinboldt W, Abildiskov J. A computer model of atrial fibrillation. Am Heart J 1962;67:200–20. - PubMed
-
- Alboni P, Scarfo S, Fuca G, et al. Hemodynamics of idiopathic paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol 1995;18:980–5. - PubMed
-
- Brignole M, Gianfranchi L, Menozzi C, et al. Assessment of atrioventricular junction ablation and DDDR mode-switching pacemaker versus pharmacological treatment in patients with severely symptomatic paroxysmal atrial fibrillation: a randomized controlled study. Circulation 1997;96:2617–24. - PubMed
-
- Marshall HJ, Harris ZI, Griffith MJ, et al. Prospective randomized study of ablation and pacing versus medical therapy for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation: effects of pacing mode and mode-switch algorithm. Circulation 1999;99:1587–92. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
