RtsA and RtsB coordinately regulate expression of the invasion and flagellar genes in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium
- PMID: 12923082
- PMCID: PMC181000
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.185.17.5096-5108.2003
RtsA and RtsB coordinately regulate expression of the invasion and flagellar genes in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium
Abstract
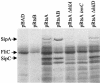
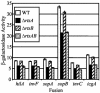
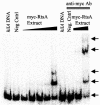
Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium encounters numerous host environments and defense mechanisms during the infection process. The bacterium responds by tightly regulating the expression of virulence genes. We identified two regulatory proteins, termed RtsA and RtsB, which are encoded in an operon located on an island integrated at tRNA(PheU) in S. enterica serovar Typhimurium. RtsA belongs to the AraC/XylS family of regulators, and RtsB is a helix-turn-helix DNA binding protein. In a random screen, we identified five RtsA-regulated fusions, all belonging to the Salmonella pathogenicity island 1 (SPI1) regulon, which encodes a type III secretion system (TTSS) required for invasion of epithelial cells. We show that RtsA increases expression of the invasion genes by inducing hilA expression. RtsA also induces expression of hilD, hilC, and the invF operon. However, induction of hilA is independent of HilC and HilD and is mediated by direct binding of RtsA to the hilA promoter. The phenotype of an rtsA null mutation is similar to the phenotype of a hilC mutation, both of which decrease expression of SPI1 genes approximately twofold. We also show that RtsA can induce expression of a SPI1 TTSS effector, slrP, independent of any SPI1 regulatory protein. RtsB represses expression of the flagellar genes by binding to the flhDC promoter region. Repression of the positive activators flhDC decreases expression of the entire flagellar regulon. We propose that RtsA and RtsB coordinate induction of invasion and repression of motility in the small intestine.
Figures



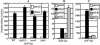

Similar articles
-
HilD, HilC and RtsA constitute a feed forward loop that controls expression of the SPI1 type three secretion system regulator hilA in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium.Mol Microbiol. 2005 Aug;57(3):691-705. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2005.04737.x. Mol Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 16045614
-
AraC/XylS family members, HilD and HilC, directly activate virulence gene expression independently of HilA in Salmonella typhimurium.Mol Microbiol. 2003 Feb;47(3):715-28. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2003.03322.x. Mol Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 12535071
-
HilD, HilC, and RtsA Form Homodimers and Heterodimers To Regulate Expression of the Salmonella Pathogenicity Island I Type III Secretion System.J Bacteriol. 2020 Apr 9;202(9):e00012-20. doi: 10.1128/JB.00012-20. Print 2020 Apr 9. J Bacteriol. 2020. PMID: 32041797 Free PMC article.
-
Adaptation to the host environment: regulation of the SPI1 type III secretion system in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2007 Feb;10(1):24-9. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2006.12.002. Epub 2007 Jan 5. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17208038 Review.
-
Salmonella invasion gene regulation: a story of environmental awareness.J Microbiol. 2005 Feb;43 Spec No:110-7. J Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 15765064 Review.
Cited by
-
Potassium transport of Salmonella is important for type III secretion and pathogenesis.Microbiology (Reading). 2013 Aug;159(Pt 8):1705-1719. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.068700-0. Epub 2013 May 31. Microbiology (Reading). 2013. PMID: 23728623 Free PMC article.
-
SNRPD2 Is a Novel Substrate for the Ubiquitin Ligase Activity of the Salmonella Type III Secretion Effector SlrP.Biology (Basel). 2022 Oct 17;11(10):1517. doi: 10.3390/biology11101517. Biology (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36290420 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping the Regulatory Network for Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium Invasion.mBio. 2016 Sep 6;7(5):e01024-16. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01024-16. mBio. 2016. PMID: 27601571 Free PMC article.
-
The Salmonella SPI1 type three secretion system responds to periplasmic disulfide bond status via the flagellar apparatus and the RcsCDB system.J Bacteriol. 2008 Jan;190(1):87-97. doi: 10.1128/JB.01323-07. Epub 2007 Oct 19. J Bacteriol. 2008. PMID: 17951383 Free PMC article.
-
In silico clustering of Salmonella global gene expression data reveals novel genes co-regulated with the SPI-1 virulence genes through HilD.Sci Rep. 2016 Nov 25;6:37858. doi: 10.1038/srep37858. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27886269 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahmer, B. M., J. van Reeuwijk, P. R. Watson, T. S. Wallis, and F. Heffron. 1999. Salmonella SirA is a global regulator of genes mediating enteropathogenesis. Mol. Microbiol. 31:971-982. - PubMed
-
- Akbar, S., L. M. Schechter, C. P. Lostroh, and C. A. Lee. 2003. AraC/XylS family members, HilD and HilC, directly activate virulence gene expression independently of HilA in Salmonella typhimurium. Mol. Microbiol. 47:715-728. - PubMed
-
- Altier, C., M. Suyemoto, A. I. Ruiz, K. D. Burnham, and R. Maurer. 2000. Characterization of two novel regulatory genes affecting Salmonella invasion gene expression. Mol. Microbiol. 35:635-646. - PubMed
-
- Ausubel, F. M. 1994. Current protocols in molecular biology. John Wiley & Sons, New York, N.Y.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

