Mutational loss of a K+ and NH4+ transporter affects the growth and endospore formation of alkaliphilic Bacillus pseudofirmus OF4
- PMID: 12923086
- PMCID: PMC181017
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.185.17.5133-5147.2003
Mutational loss of a K+ and NH4+ transporter affects the growth and endospore formation of alkaliphilic Bacillus pseudofirmus OF4
Abstract
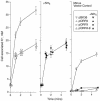
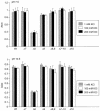
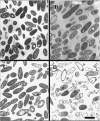
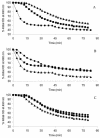
A putative transport protein (Orf9) of alkaliphilic Bacillus pseudofirmus OF4 belongs to a transporter family (CPA-2) of diverse K+ efflux proteins and cation antiporters. Orf9 greatly increased the concentration of K+ required for growth of a K+ uptake mutant of Escherichia coli. The cytoplasmic K+ content of the cells was reduced, consistent with an efflux mechanism. Orf9-dependent translocation of K+ in E. coli is apparently bidirectional, since ammonium-sensitive uptake of K+ could be shown in K+ -depleted cells. The upstream gene product Orf8 has sequence similarity to a subdomain of KTN proteins that are associated with potassium-translocating channels and transporters; Orf8 modulated the transport capacities of Orf9. No Orf9-dependent K+(Na+)/H+ antiport activity was found in membrane vesicles. Nonpolar deletion mutants in the orf9 locus of the alkaliphile chromosome exhibited no K+ -related phenotype but showed profound phenotypes in medium containing high levels of amine-nitrogen. Their patterns of growth and ammonium content suggested a physiological role for the orf9 locus in bidirectional ammonium transport. Orf9-dependent ammonium uptake was observed in right-side-out membrane vesicles of the alkaliphile wild type and the mutant with an orf8 deletion. Uptake was proton motive force dependent and was inhibited by K+. Orf9 is proposed to be designated AmhT (ammonium homeostasis). Ammonium homeostasis is important in high-amine-nitrogen settings and is particularly crucial at high pH since cytosolic ammonium accumulation interferes with cytoplasmic pH regulation. Endospore formation in amino-acid-rich medium was significantly defective and germination was modestly defective in the orf9 and orf7-orf10 deletion mutants.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Two types of Bacillus subtilis tetA(L) deletion strains reveal the physiological importance of TetA(L) in K(+) acquisition as well as in Na(+), alkali, and tetracycline resistance.J Bacteriol. 2000 Apr;182(8):2088-95. doi: 10.1128/JB.182.8.2088-2095.2000. J Bacteriol. 2000. PMID: 10735849 Free PMC article.
-
GerN, an endospore germination protein of Bacillus cereus, is an Na(+)/H(+)-K(+) antiporter.J Bacteriol. 2001 Oct;183(20):5896-903. doi: 10.1128/JB.183.20.5896-5903.2001. J Bacteriol. 2001. PMID: 11566988 Free PMC article.
-
Cloning and characterization of a putative Ca2+/H+ antiporter gene from Escherichia coli upon functional complementation of Na+/H+ antiporter-deficient strains by the overexpressed gene.J Biol Chem. 1993 May 25;268(15):11296-303. J Biol Chem. 1993. PMID: 8496184
-
pH homeostasis and ATP synthesis: studies of two processes that necessitate inward proton translocation in extremely alkaliphilic Bacillus species.Extremophiles. 1998 Aug;2(3):217-22. doi: 10.1007/s007920050063. Extremophiles. 1998. PMID: 9783168 Review.
-
The role of monovalent cation/proton antiporters in Na(+)-resistance and pH homeostasis in Bacillus: an alkaliphile versus a neutralophile.J Exp Biol. 1994 Nov;196:457-70. doi: 10.1242/jeb.196.1.457. J Exp Biol. 1994. PMID: 7823040 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative analysis of reconstructed ancestral proteins with their extant counterparts suggests primitive life had an alkaline habitat.Sci Rep. 2024 Jan 3;14(1):398. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-50828-4. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38172176 Free PMC article.
-
A Bacillus flagellar motor that can use both Na+ and K+ as a coupling ion is converted by a single mutation to use only Na+.PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e46248. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0046248. Epub 2012 Sep 25. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23049994 Free PMC article.
-
Metabacillus dongyingensis sp. nov. Is Represented by the Plant Growth-Promoting Bacterium BY2G20 Isolated from Saline-Alkaline Soil and Enhances the Growth of Zea mays L. under Salt Stress.mSystems. 2022 Apr 26;7(2):e0142621. doi: 10.1128/msystems.01426-21. Epub 2022 Mar 1. mSystems. 2022. PMID: 35229649 Free PMC article.
-
Three putative cation/proton antiporters from the soda lake alkaliphile Alkalimonas amylolytica N10 complement an alkali-sensitive Escherichia coli mutant.Microbiology (Reading). 2007 Jul;153(Pt 7):2168-2179. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.2007/007450-0. Microbiology (Reading). 2007. PMID: 17600061 Free PMC article.
-
The Emergence of 2-Oxoglutarate as a Master Regulator Metabolite.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2015 Dec;79(4):419-35. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00038-15. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2015. PMID: 26424716 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alekshun, M. N., S. B. Levy, T. R. Mealy, B. A. Seaton, and J. F. Head. 2001. The crystal structure of MarR, a regulator of multiple antibiotic resistance, at 2.3 Å resolution. Nat. Struct. Biol. 8:710-714. - PubMed
-
- Ambudkar, S. V., G. U. Zlotnick, and B. P. Rosen. 1984. Calcium efflux from Escherichia coli: evidence for two systems. J. Biol. Chem. 259:6142-6146. - PubMed
-
- Anantharaman, V., E. V. Koonin, and L. Aravind. 2001. Regulatory potential, phyletic distribution and evolution of ancient, intracellular small-molecule-binding domains. J. Mol. Biol. 307:1271-1292. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

