Mutant MiRP1 subunits modulate HERG K+ channel gating: a mechanism for pro-arrhythmia in long QT syndrome type 6
- PMID: 12923204
- PMCID: PMC2343156
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2003.046045
Mutant MiRP1 subunits modulate HERG K+ channel gating: a mechanism for pro-arrhythmia in long QT syndrome type 6
Abstract
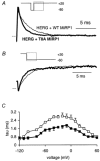
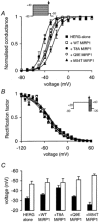
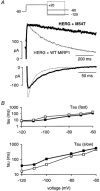
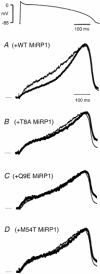
Mutations in KCNE2, which encodes the minK-related protein 1 (MiRP1), are associated with an increased risk of arrhythmias; however, the underlying mechanisms are unknown. MiRP1 is thought to associate with many K+ channel alpha-subunits, including HERG K+ channels, which have a major role in suppressing arrhythmias initiated by premature beats. In this study we have investigated in Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells at 37 degrees C the effects of co-expressing HERG K+ channels with either wild-type (WT) MiRP1 or one of three mutant MiRP1 subunits, T8A, Q9E and M54T. The most significant effects of MiRP1 subunits on HERG channels were a more negative steady-state activation for HERG + T8A MiRP1 and a more positive steady-state activation for HERG + M54T MiRP1 compared to either HERG + WT MiRP1 or HERG alone. All three mutants caused a significant slowing of deactivation at depolarised potentials. T8A MiRP1 also caused an acceleration of inactivation and recovery from inactivation compared to HERG + WT MiRP1. During ventricular action potential clamp experiments there was a significant decrease in current in the early phases of the action potential for HERG + WT MiRP1 channels compared to HERG alone. This effect was not as prominent for the mutant MiRP1 subunits. During premature action potential clamp protocols, the T8A and Q9E mutants, but not the M54T mutant, resulted in significantly larger current spikes during closely coupled premature beats, compared to HERG + WT MiRP1. At longer coupling intervals, all three mutants resulted in larger current spikes than HERG alone or HERG + WT MiRP1 channels. It is therefore possible that augmentation of HERG currents in the early diastolic period may be pro-arrhythmic.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Identification and functional characterization of a novel KCNE2 (MiRP1) mutation that alters HERG channel kinetics.J Mol Med (Berl). 2002 Aug;80(8):524-32. doi: 10.1007/s00109-002-0364-0. Epub 2002 Jun 28. J Mol Med (Berl). 2002. PMID: 12185453
-
HERG mutation predicts short QT based on channel kinetics but causes long QT by heterotetrameric trafficking deficiency.Cardiovasc Res. 2005 Aug 15;67(3):467-75. doi: 10.1016/j.cardiores.2005.05.017. Cardiovasc Res. 2005. PMID: 15958262
-
Local anaesthetic sensitivities of cloned HERG channels from human heart: comparison with HERG/MiRP1 and HERG/MiRP1 T8A.Br J Anaesth. 2004 Jan;92(1):93-101. doi: 10.1093/bja/aeh026. Br J Anaesth. 2004. PMID: 14665560
-
Does hERG coassemble with a beta subunit? Evidence for roles of MinK and MiRP1.Novartis Found Symp. 2005;266:100-12; discussion 112-7, 155-8. Novartis Found Symp. 2005. PMID: 16050264 Review.
-
Two components of delayed rectifier K+ current in heart: molecular basis, functional diversity, and contribution to repolarization.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2004 Feb;25(2):137-45. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2004. PMID: 14769199 Review.
Cited by
-
HERG1 channelopathies.Pflugers Arch. 2010 Jul;460(2):265-76. doi: 10.1007/s00424-009-0758-8. Epub 2009 Nov 22. Pflugers Arch. 2010. PMID: 20544339 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potassium-channel mutations and cardiac arrhythmias--diagnosis and therapy.Nat Rev Cardiol. 2012 Jan 31;9(6):319-32. doi: 10.1038/nrcardio.2012.3. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2012. PMID: 22290238 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Calcium Handling Defects and Cardiac Arrhythmia Syndromes.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Feb 25;11:72. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00072. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32161540 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular basis of slow activation of the human ether-a-go-go related gene potassium channel.J Physiol. 2004 Jul 15;558(Pt 2):417-31. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2004.062588. Epub 2004 Jun 4. J Physiol. 2004. PMID: 15181157 Free PMC article.
-
A temperature-dependent in silico model of the human ether-à-go-go-related (hERG) gene channel.J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods. 2016 Sep-Oct;81:233-9. doi: 10.1016/j.vascn.2016.05.005. Epub 2016 May 11. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods. 2016. PMID: 27178106 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abbott GW, Goldstein SA, Sesti F. Do all voltage-gated potassium channels use MiRPs? Circ Res. 2001;88:981–983. - PubMed
-
- Abbott GW, Sesti F, Splawski I, Buck ME, Lehmann MH, Timothy KW, Keating MT, Goldstein SA. MiRP1 forms IKr potassium channels with HERG and is associated with cardiac arrhythmia. Cell. 1999;97:175–187. - PubMed
-
- Balser JR. Sodium ‘channelopathies’ and sudden death: must you be so sensitive? Circ Res. 1999;85:872–874. - PubMed
-
- Cui J, Melman Y, Palma E, Fishman Gi, McDonald TV. Cyclic AMP regulates the HERG K(+) channel by dual pathways. Curr Biol. 2000;10:671–674. - PubMed
-
- Curran ME, Splawski I, Timothy KW, Vincent GM, Green ED, Keating MT. A molecular basis for cardiac arrhythmia: HERG mutations cause long QT syndrome. Cell. 1995;80:795–803. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

