The B cell receptor itself can activate complement to provide the complement receptor 1/2 ligand required to enhance B cell immune responses in vivo
- PMID: 12925675
- PMCID: PMC2194168
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20022042
The B cell receptor itself can activate complement to provide the complement receptor 1/2 ligand required to enhance B cell immune responses in vivo
Abstract
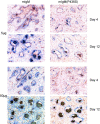
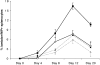
B cells express complement receptors (CRs) that bind activated fragments of C3 and C4. Immunized CR knockout (KO) mice have lower antibody titers and smaller germinal centers (GCs), demonstrating the importance of CR signals for the humoral immune response. CR ligands were thought to be generated via complement fixation mediated by preexisting "natural" IgM or early Ab from inefficiently activated B cells. This concept was recently challenged by a transgenic (Tg) mouse model that lacks circulating antibody but still retains membrane IgM (mIgM) and mounts normal immune responses. To test whether CR ligands could be generated by the B cell receptor (BCR) itself, we generated similar mice carrying a mutated mIgM that was defective in C1q binding. We found that B cells from such mutant mice do not deposit C3 on B cells upon BCR ligation, in contrast to B cells from mIgM mice. This has implications for the immune response: the mutant mice have smaller GCs than mIgM mice, and they are particularly deficient in the maintenance of the GC response. These results demonstrate a new BCR-dependent pathway that is sufficient and perhaps necessary to provide a CR1/2 ligand that promotes efficient B cell activation.
Figures



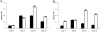

References
-
- Carter, R.H., M.O. Spycher, Y.C. Ng, R. Hoffman, and D.T. Fearon. 1988. Synergistic interaction between complement receptor type 2 and membrane IgM on B lymphocytes. J. Immunol. 141:457–463. - PubMed
-
- Pepys, M.B. 1972. Role of complement in induction of the allergic response. Nat. New Biol. 237:157–159. - PubMed
-
- Chen, Z., S.B. Koralov, M. Gendelman, M.C. Carroll, and G. Kelsoe. 2000. Humoral immune responses in Cr2−/− mice: enhanced affinity maturation but impaired antibody persistence. J. Immunol. 164:4522–4532. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

