Tuberculosis toxin blocking phagosome maturation inhibits a novel Ca2+/calmodulin-PI3K hVPS34 cascade
- PMID: 12925680
- PMCID: PMC2194170
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20030527
Tuberculosis toxin blocking phagosome maturation inhibits a novel Ca2+/calmodulin-PI3K hVPS34 cascade
Abstract
The capacity of Mycobacterium tuberculosis to infect latently over one billion people and cause two million fatalities annually rests with its ability to block phagosomal maturation into the phagolysosome in infected macrophages. Here we describe how M. tuberculosis toxin lipoarabinomannan (LAM) causes phagosome maturation arrest, interfering with a new pathway connecting intracellular signaling and membrane trafficking. LAM from virulent M. tuberculosis, but not from avirulent mycobacteria, blocked cytosolic Ca2+ increase. Ca2+ and calmodulin were required for a newly uncovered Ca2+/calmodulin phosphatidylinositol (PI)3 kinase hVPS34 cascade, essential for production of PI 3 phosphate (PI3P) on liposomes in vitro and on phagosomes in vivo. The interference of the trafficking toxin LAM with the calmodulin-dependent production of PI3P described here ensures long-term M. tuberculosis residence in vacuoles sequestered away from the bactericidal and antigen-processing organelles in infected macrophages.
Figures
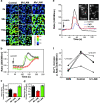
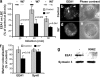
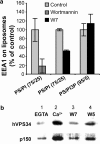
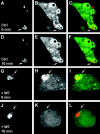
References
-
- Meresse, S., O. Steele-Mortimer, E. Moreno, M. Desjardins, B. Finlay, and J.P. Gorvel. 1999. Controlling the maturation of pathogen-containing vacuoles: a matter of life and death. Nat. Cell Biol. 1:E183–E188. - PubMed
-
- Christoforidis, S., H.M. McBride, R.D. Burgoyne, and M. Zerial. 1999. The Rab5 effector EEA1 is a core component of endosome docking. Nature. 397:621–625. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

