The enigma of sepsis
- PMID: 12925683
- PMCID: PMC171398
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI19523
The enigma of sepsis
Abstract
Sepsis remains a serious cause of morbidity and mortality, and the pathophysiology of the disease is not clear. The definition of the clinical manifestations of sepsis is ever evolving. This review discusses the search for effective therapeutic interventions, hurdles in translational sepsis research, and new therapies in development in current clinical trials.
Figures
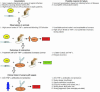
References
-
- Angus DC, et al. Epidemiology of severe sepsis in the United States: analysis of incidence, outcome, and associated costs of care. Crit. Care Med. 2001;29:1303–1310. - PubMed
-
- Martin GS, Mannino DM, Eaton S, Moss M. The epidemiology of sepsis in the United States from 1979 through 2000. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003;348:1546–1554. - PubMed
-
- Eichacker PQ, et al. Risk and the efficacy of antiinflammatory agents: retrospective and confirmatory studies of sepsis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002;166:1197–1205. - PubMed
-
- Bone RC, et al. Sepsis syndrome: a valid clinical entity. Methylprednisolone Severe Sepsis Study Group. Crit. Care Med. 1989;17:389–393. - PubMed
-
- Goris RJ, te Boekhorst TP, Nuytinck JK, Gimbráere JS. Multiple-organ failure. Generalized autodestructive inflammation? Arch. Surg. 1985;120:1109–1115. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

