Thyroid hormone action in the absence of thyroid hormone receptor DNA-binding in vivo
- PMID: 12925699
- PMCID: PMC171393
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI18377
Thyroid hormone action in the absence of thyroid hormone receptor DNA-binding in vivo
Abstract
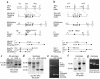
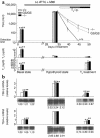
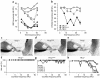
Thyroid hormone action is mediated by thyroid hormone receptors (TRs), which are members of the nuclear hormone receptor superfamily. DNA-binding is presumed to be essential for all nuclear actions of thyroid hormone. To test this hypothesis in vivo, the DNA-binding domain of TR-beta was mutated within its P-box (GS mutant) using gene targeting techniques. This mutation in vitro completely abolishes TR-beta DNA-binding, while preserving ligand (T3) and cofactor interactions with the receptor. Homozygous mutant (TR-betaGS/GS) mice displayed abnormal T3 regulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid axis and retina identical to abnormalities previously observed in TR-beta KO (TR-beta-/-) mice. However, TR-betaGS/GS mutant mice maintained normal hearing at certain frequencies and did not display significant outer hair cell loss, in contrast to TR-beta-/- mice. DNA-binding, therefore, is essential for many functions of the TR, including retinal development and negative feedback regulation by thyroid hormone of the hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid axis. Inner ear development, although not completely normal, can occur in the absence of TR DNA-binding, suggesting that an alternative and perhaps novel thyroid hormone-signaling pathway may mediate these effects.
Figures


Comment in
-
Thyroid hormone action: a binding contract.J Clin Invest. 2003 Aug;112(4):497-9. doi: 10.1172/JCI19479. J Clin Invest. 2003. PMID: 12925689 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Brent GA. The molecular basis of thyroid hormone action. N. Engl. J. Med. 1994;331:847–853. - PubMed
-
- Oppenheimer JH, Schwartz HL. Molecular basis of thyroid hormone-dependent brain development. Endocr. Rev. 1997;18:462–475. - PubMed
-
- Koibuchi N, Chin WW. Thyroid hormone action and brain development. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2000;11:123–128. - PubMed
-
- Cohen, R.C., Weintraub, B.D., and Wondisford, F.E. 2000. Chemistry and biosynthesis of thyrotropin. In Werner and Ingbar’s The thyroid: a fundamental and clinical text. 8th edition. L.E. Braverman, and R.D. Utiger, editors. Williams & Wilkins. Baltimore, Maryland, USA. 202–218.
-
- Forrest D, Erway LC, Ng L, Altschuler R, Curran T. Thyroid hormone receptor beta is essential for development of auditory function. Nat. Genet. 1996;13:354–357. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

