Regulation of insulin-like growth factor-dependent myoblast differentiation by Foxo forkhead transcription factors
- PMID: 12925703
- PMCID: PMC2173790
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200212107
Regulation of insulin-like growth factor-dependent myoblast differentiation by Foxo forkhead transcription factors
Abstract
Insulin-like growth factors promote myoblast differentiation through phosphoinositol 3-kinase and Akt signaling. Akt substrates required for myogenic differentiation are unknown. Forkhead transcription factors of the forkhead box gene, group O (Foxo) subfamily are phosphorylated in an insulin-responsive manner by phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-dependent kinases. Phosphorylation leads to nuclear exclusion and inactivation. We show that a constitutively active Foxo1 mutant inhibits differentiation of C2C12 cells and prevents myotube differentiation induced by constitutively active Akt. In contrast, a transcriptionally inactive mutant Foxo1 partially rescues inhibition of C2C12 differentiation mediated by wortmannin, but not by rapamycin, and is able to induce aggregation-independent myogenic conversion of teratocarcinoma cells. Inhibition of Foxo expression by siRNA resulted in more efficient differentiation, associated with increased myosin expression. These observations indicate that Foxo proteins are key effectors of Akt-dependent myogenesis.
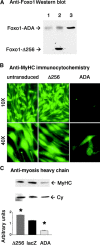
Figures




Similar articles
-
Nuclear exclusion of forkhead box O and Elk1 and activation of nuclear factor-kappaB are required for C2C12-RasV12C40 myoblast differentiation.Endocrinology. 2008 Feb;149(2):793-801. doi: 10.1210/en.2007-0657. Epub 2007 Oct 25. Endocrinology. 2008. PMID: 17962350
-
Leucine promotes differentiation of porcine myoblasts through the protein kinase B (Akt)/Forkhead box O1 signalling pathway.Br J Nutr. 2018 Apr;119(7):727-733. doi: 10.1017/S0007114518000181. Br J Nutr. 2018. PMID: 29569540
-
Regulation of cardiomyocyte proliferation and myocardial growth during development by FOXO transcription factors.Circ Res. 2008 Mar 28;102(6):686-94. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.107.163428. Epub 2008 Jan 24. Circ Res. 2008. PMID: 18218983
-
FoxO transcription factors; Regulation by AKT and 14-3-3 proteins.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011 Nov;1813(11):1938-45. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2011.06.002. Epub 2011 Jun 17. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011. PMID: 21708191 Review.
-
FOXO transcription factors: from cell fate decisions to regulation of human female reproduction.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2009;665:227-41. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4419-1599-3_17. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2009. PMID: 20429428 Review.
Cited by
-
Methylation by Set9 modulates FoxO3 stability and transcriptional activity.Aging (Albany NY). 2012 Jul;4(7):462-79. doi: 10.18632/aging.100471. Aging (Albany NY). 2012. PMID: 22820736 Free PMC article.
-
Reprogramming Cells to Make Insulin.J Endocr Soc. 2019 Apr 24;3(6):1214-1226. doi: 10.1210/js.2019-00040. eCollection 2019 Jun 1. J Endocr Soc. 2019. PMID: 31187080 Free PMC article. Review.
-
FoxOs: Unifying links between oxidative stress and skeletal homeostasis.Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2011 Jun;9(2):60-6. doi: 10.1007/s11914-011-0054-3. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2011. PMID: 21404001 Review.
-
Tissue expression of porcine FoxO1 and its negative regulation during primary preadipocyte differentiation.Mol Biol Rep. 2009 Jan;36(1):165-76. doi: 10.1007/s11033-007-9163-6. Epub 2008 Feb 22. Mol Biol Rep. 2009. PMID: 18293098
-
The FOXO's Advantages of Being a Family: Considerations on Function and Evolution.Cells. 2020 Mar 24;9(3):787. doi: 10.3390/cells9030787. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32214027 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Astolfi, A., C. De Giovanni, L. Landuzzi, G. Nicoletti, C. Ricci, S. Croci, L. Scopece, P. Nanni, and P.L. Lollini. 2001. Identification of new genes related to the myogenic differentiation arrest of human rhabdomyosarcoma cells. Gene. 274:139–149. - PubMed
-
- Brunet, A., A. Bonni, M.J. Zigmond, M.Z. Lin, P. Juo, L.S. Hu, M.J. Anderson, K.C. Arden, J. Blenis, and M.E. Greenberg. 1999. Akt promotes cell survival by phosphorylating and inhibiting a forkhead transcription factor. Cell. 96:857–868. - PubMed
-
- Canicio, J., E. Gallardo, I. Illa, X. Testar, M. Palacin, A. Zorzano, and P. Kaliman. 1998. p70 S6 kinase activation is not required for insulin-like growth factor-induced differentiation of rat, mouse, or human skeletal muscle cells. Endocrinology. 139:5042–5049. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

