Degradation of p57Kip2 mediated by SCFSkp2-dependent ubiquitylation
- PMID: 12925736
- PMCID: PMC193544
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1831009100
Degradation of p57Kip2 mediated by SCFSkp2-dependent ubiquitylation
Abstract
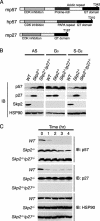
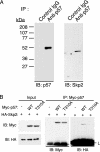
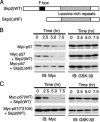
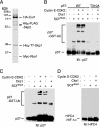
The abundance of the cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) inhibitor p57Kip2, an important regulator of cell cycle progression, is thought to be controlled by the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. The Skp1/Cul1/F-box (SCF)-type E3 ubiquitin ligase complex SCFSkp2 has now been shown to be responsible for regulating the cellular level of p57Kip2 by targeting it for ubiquitylation and proteolysis. The elimination of p57Kip2 was impaired in Skp2-/- cells, resulting in abnormal accumulation of the protein. Coimmunoprecipitation analysis also revealed that Skp2 interacts with p57Kip2 in vivo. Overexpression of WT Skp2 promoted degradation of p57Kip2, whereas expression of a dominant negative mutant of Skp2 prolonged the half-life of p57Kip2. Mutation of the threonine residue (Thr-310) of human p57Kip2 that is conserved between the COOH-terminal QT domains of p57Kip2 and p27Kip1 prevented the effect of Skp2 on the stability of p57Kip2, suggesting that phosphorylation at this site is required for SCFSkp2-mediated ubiquitylation. Finally, the purified recombinant SCFSkp2 complex mediated p57Kip2 ubiquitylation in vitro in a manner dependent on the presence of the cyclin E-CDK2 complex. These observations thus demonstrate that the SCFSkp2 complex plays an important role in cell-cycle progression by determining the abundance of p57Kip2 and that of the related CDK inhibitor p27Kip1.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The pRb-related protein p130 is regulated by phosphorylation-dependent proteolysis via the protein-ubiquitin ligase SCF(Skp2).Genes Dev. 2002 Nov 15;16(22):2946-57. doi: 10.1101/gad.1011202. Genes Dev. 2002. PMID: 12435635 Free PMC article.
-
The F-box protein SKP2 mediates androgen control of p27 stability in LNCaP human prostate cancer cells.BMC Cell Biol. 2002 Aug 20;3:22. doi: 10.1186/1471-2121-3-22. Epub 2002 Aug 20. BMC Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 12188931 Free PMC article.
-
Degradation of p27(Kip1) at the G(0)-G(1) transition mediated by a Skp2-independent ubiquitination pathway.J Biol Chem. 2001 Dec 28;276(52):48937-43. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M107274200. Epub 2001 Oct 26. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11682478
-
Regulation of the cell cycle at the G1-S transition by proteolysis of cyclin E and p27Kip1.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001 Apr 13;282(4):853-60. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.2001.4627. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001. PMID: 11352628 Review.
-
Ubiquitin ligases in malignant lymphoma.Leuk Lymphoma. 2004 Jul;45(7):1329-39. doi: 10.1080/10428190410001663635. Leuk Lymphoma. 2004. PMID: 15359630 Review.
Cited by
-
A patent review of the ubiquitin ligase system: 2015-2018.Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2018 Dec;28(12):919-937. doi: 10.1080/13543776.2018.1549229. Epub 2018 Nov 23. Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2018. PMID: 30449221 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Skp2 stabilizes Mcl-1 and confers radioresistance in colorectal cancer.Cell Death Dis. 2022 Mar 18;13(3):249. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-04685-0. Cell Death Dis. 2022. PMID: 35301297 Free PMC article.
-
The activity and stability of the intrinsically disordered Cip/Kip protein family are regulated by non-receptor tyrosine kinases.J Mol Biol. 2015 Jan 30;427(2):371-386. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2014.11.011. Epub 2014 Nov 20. J Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25463440 Free PMC article.
-
CIP/KIP and INK4 families as hostages of oncogenic signaling.Cell Div. 2024 Apr 1;19(1):11. doi: 10.1186/s13008-024-00115-z. Cell Div. 2024. PMID: 38561743 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endoreplication.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013 Jan 1;5(1):a012948. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a012948. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013. PMID: 23284048 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hershko, A. & Ciechanover, A. (1998) Annu. Rev. Biochem. 67, 425-479. - PubMed
-
- Hochstrasser, M. (1996) Annu. Rev. Genet. 30, 405-439. - PubMed
-
- Joazeiro, C. A. & Weissman, A. M. (2000) Cell 102, 549-552. - PubMed
-
- Hatakeyama, S., Yada, M., Matsumoto, M., Ishida, N. & Nakayama, K. I. (2001) J. Biol. Chem. 276, 33111-33120. - PubMed
-
- Aravind, L. & Koonin, E. V. (2000) Curr. Biol. 10, R132-R134. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

