A noncanonical sequence phosphorylated by casein kinase 1 in beta-catenin may play a role in casein kinase 1 targeting of important signaling proteins
- PMID: 12925738
- PMCID: PMC193538
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1733909100
A noncanonical sequence phosphorylated by casein kinase 1 in beta-catenin may play a role in casein kinase 1 targeting of important signaling proteins
Abstract
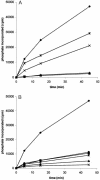
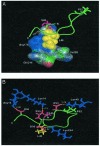
Protein kinase casein kinase 1 (CK1) phosphorylates Ser-45 of beta-catenin, "priming" the subsequent phosphorylation by glycogen synthase-3 of residues 41, 37, and 33. This concerted phosphorylation of beta-catenin signals its degradation and prevents its function in triggering cell division. The sequence around Ser-45 does not conform to the canonical consensus for CK1 substrates, which prescribes either phosphoamino acids or acidic residues in position n-3 from the target serine. However, the beta-catenin sequence downstream from Ser-45 is very similar to a sequence recognized by CK1 in nuclear factor for activated T cells 4. The common features include an SLS motif followed two to five residues downstream by a cluster of acidic residues. Synthetic peptides reproducing residues 38-65 of beta-catenin were assayed with purified rat liver CK1 or recombinant CK1 alpha and CK1 alpha L from zebrafish. The results demonstrate that SLS and acidic cluster motifs are crucial for CK1 recognition. Pro-44 and Pro-52 are also important for efficient phosphorylation. Similar results were obtained with the different isoforms of CK1. Phosphorylation of mutants of full-length recombinant beta-catenin from zebrafish confirmed the importance of the SLS and acidic cluster motifs. A search for proteins with similar motifs yielded, among other proteins, adenomatous polyposis coli, previously found to be phosphorylated by CK1. There is a strong correlation of beta-catenin mutations found in thyroid tumors with the motifs recognized by CK1 in this protein.
Figures

References
-
- Appella, E. & Anderson, C. W. (2001) Eur. J. Biochem. 268, 2764-2772. - PubMed
-
- Flotow, H., Graves, P. R., Wang, A., Fiol, C. J., Roeske, R. W. & Roach, P. J. (1990) J. Biol. Chem. 265, 14264-14269. - PubMed
-
- Meggio, F., Perich, J. W., Reynolds, E. C. & Pinna, L. A. (1991) FEBS Lett. 283, 303-306. - PubMed
-
- Harwood, A. J. (2001) Cell 105, 821-824. - PubMed
-
- Dajani, R., Fraser, E., Roe, S. M., Young, N., Good, V., Dale, T. C. & Pearl, L. H. (2001) Cell 105, 721-732. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

