Unique and conserved features of genome and proteome of SARS-coronavirus, an early split-off from the coronavirus group 2 lineage
- PMID: 12927536
- PMCID: PMC7159028
- DOI: 10.1016/s0022-2836(03)00865-9
Unique and conserved features of genome and proteome of SARS-coronavirus, an early split-off from the coronavirus group 2 lineage
Abstract
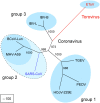
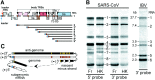
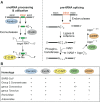
The genome organization and expression strategy of the newly identified severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV) were predicted using recently published genome sequences. Fourteen putative open reading frames were identified, 12 of which were predicted to be expressed from a nested set of eight subgenomic mRNAs. The synthesis of these mRNAs in SARS-CoV-infected cells was confirmed experimentally. The 4382- and 7073 amino acid residue SARS-CoV replicase polyproteins are predicted to be cleaved into 16 subunits by two viral proteinases (bringing the total number of SARS-CoV proteins to 28). A phylogenetic analysis of the replicase gene, using a distantly related torovirus as an outgroup, demonstrated that, despite a number of unique features, SARS-CoV is most closely related to group 2 coronaviruses. Distant homologs of cellular RNA processing enzymes were identified in group 2 coronaviruses, with four of them being conserved in SARS-CoV. These newly recognized viral enzymes place the mechanism of coronavirus RNA synthesis in a completely new perspective. Furthermore, together with previously described viral enzymes, they will be important targets for the design of antiviral strategies aimed at controlling the further spread of SARS-CoV.
Figures


References
-
- Ksiazek T.G., Erdman D., Goldsmith C.S., Zaki S.R., Peret T., Emery S. A novel coronavirus associated with severe acute respiratory syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003;348:1953–1966. - PubMed
-
- Drosten C., Gunther S., Preiser W., van der Werf S., Brodt H.R., Becker S. Identification of a novel coronavirus in patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003;348:1967–1976. - PubMed
-
- Marra M.A., Jones S.J., Astell C.R., Holt R.A., Brooks-Wilson A., Butterfield Y.S. The Genome sequence of the SARS-associated coronavirus. Science. 2003;300:1399–1404. - PubMed
-
- Rota P.A., Oberste M.S., Monroe S.S., Nix W.A., Campagnoli R., Icenogle J.P. Characterization of a novel coronavirus associated with severe acute respiratory syndrome. Science. 2003;300:1394–1399. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

