Unilateral carrageenan injection into muscle or joint induces chronic bilateral hyperalgesia in rats
- PMID: 12927629
- PMCID: PMC2732018
- DOI: 10.1016/S0304-3959(03)00114-3
Unilateral carrageenan injection into muscle or joint induces chronic bilateral hyperalgesia in rats
Abstract
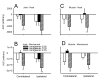
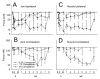
Chronic musculoskeletal pain is a major clinical problem and there is a general lack of animal models to study this condition. Carrageenan is commonly used to produce short-lasting acute inflammation and hyperalgesia in animal models. However, the potential of carrageenan to produce chronic, long-lasting hyperalgesia has not been evaluated. In the present study, we investigated the long-term effects of carrageenan injected into joint or muscle in rats. Rats were injected with 0.3, 1 or 3% carrageenan in one knee joint or gastrocnemius muscle and hyperalgesia to mechanical (measured as decreased withdrawal threshold) and heat (measured as decreased withdrawal latency) stimuli of both paws assessed before and at varying times after injection, through 8 weeks. Histological changes were examined only after injection of 3% carrageenan. Three percent carrageenan injected in the muscle or knee produced hyperalgesia to mechanical and heat stimuli ipsilaterally, which lasted 7-8 weeks and spread to the contralateral side 1-2 weeks after injection. One percent carrageenan injected to the knee joint or gastrocnemius muscle, produced hyperalgesia that was shorter-lasting and remained ipsilateral; 0.3% carrageenan injected into the knee joint or gastrocnemius muscle had no effect. Three percent carrageenan injected into the skin surrounding the knee joint did not produce hyperalgesia. A similar pattern of inflammatory changes was observed histologically for both the joint and muscle tissues. Acute inflammation was observed for the first 24 h with edema and neutrophilic infiltration evident as early as 4 h. At 1 week, the inflammation converted to primarily a macrophage response with scattered mast cells. The data suggest that animals injected with 1 or 3% carrageenan in the knee joint or gastrocnemius muscle could be used as models of acute inflammation through 24 h and chronic inflammation after 1 week. Furthermore, 3% carrageenan injected into deep tissues produces hyperalgesia that spreads to the contralateral side, at the same time period as the inflammation transforms from acute to chronic.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Characterization of a method for measuring primary hyperalgesia of deep somatic tissue.J Pain. 2005 Jan;6(1):41-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jpain.2004.10.002. J Pain. 2005. PMID: 15629417
-
Pharmacological characterization of carrageenan induced heat muscle hyperalgesia in rats using non-selective, preferential and selective COX-2 inhibitors.Pharmacol Rep. 2014 Jun;66(3):353-62. doi: 10.1016/j.pharep.2013.12.011. Epub 2014 Apr 13. Pharmacol Rep. 2014. PMID: 24905509
-
Characterization of the nociceptive effect of carrageenan: Masseter versus gastrocnemius.Muscle Nerve. 2017 Oct;56(4):804-813. doi: 10.1002/mus.25538. Epub 2017 Apr 25. Muscle Nerve. 2017. PMID: 28026014
-
Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) reduces chronic hyperalgesia induced by muscle inflammation.Pain. 2006 Jan;120(1-2):182-187. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2005.10.030. Epub 2005 Dec 19. Pain. 2006. PMID: 16360266
-
Pregabalin reduces muscle and cutaneous hyperalgesia in two models of chronic muscle pain in rats.J Pain. 2007 May;8(5):422-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jpain.2006.11.007. Epub 2007 Feb 9. J Pain. 2007. PMID: 17293165
Cited by
-
Nuclear factor-kappa B regulates pain and COMT expression in a rodent model of inflammation.Brain Behav Immun. 2015 Nov;50:196-202. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2015.07.014. Epub 2015 Jul 15. Brain Behav Immun. 2015. PMID: 26187567 Free PMC article.
-
Blockade of opioid receptors in the medullary reticularis nucleus dorsalis, but not the rostral ventromedial medulla, prevents analgesia produced by diffuse noxious inhibitory control in rats with muscle inflammation.J Pain. 2011 Jun;12(6):687-97. doi: 10.1016/j.jpain.2010.12.009. Epub 2011 Feb 17. J Pain. 2011. PMID: 21330219 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of wheel-running using the upper limbs following immobilization after inducing arthritis in the knees of rats.Physiol Res. 2021 Mar 17;70(1):79-87. doi: 10.33549/physiolres.934469. Epub 2021 Jan 14. Physiol Res. 2021. PMID: 33453715 Free PMC article.
-
Muscle inflammation induces a protein kinase Cepsilon-dependent chronic-latent muscle pain.J Pain. 2008 May;9(5):457-62. doi: 10.1016/j.jpain.2008.01.328. Epub 2008 Mar 14. J Pain. 2008. PMID: 18342576 Free PMC article.
-
Real-time application of the Rat Grimace Scale as a welfare refinement in laboratory rats.Sci Rep. 2016 Aug 17;6:31667. doi: 10.1038/srep31667. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27530823 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bendele A, McComb J, Gould T, McAbee T, Sennello G, Chlipala E, Guy M. Animal models of arthritis: relevance to human disease. Toxicol Pathol. 1999;27:134–42. - PubMed
-
- Berberich P, Hoheisel U, Mense S. Effects of a carrageenan-induced myositis on the discharge properties of group III and IV muscle receptors in the cat. J Neurophysiol. 1988;59:1395–409. - PubMed
-
- Bileviciute I, Lundeberg T, Ekblom A, Theodorsson E. Bilateral changes of substance P-, neurokinin A-, calcitonin gene-related peptide- and neuropeptide Y-like immunoreactivity in rat knee joint synovial fluid during acute monoarthritis. Neurosci Lett. 1993;153:37–40. - PubMed
-
- Chacur M, Milligan ED, Gazda LS, Armstrong C, Wang H, Tracey KJ, Maier SF, Watkins LR. A new model of sciatic inflammatory neuritis (SIN): induction of unilateral and bilateral mechanical allodynia following acute unilateral peri-sciatic immune activation in rats. Pain. 2001;94:231–44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

