Genomewide linkage scan for schizophrenia susceptibility loci among Ashkenazi Jewish families shows evidence of linkage on chromosome 10q22
- PMID: 12929083
- PMCID: PMC1180684
- DOI: 10.1086/378158
Genomewide linkage scan for schizophrenia susceptibility loci among Ashkenazi Jewish families shows evidence of linkage on chromosome 10q22
Abstract
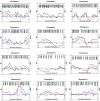
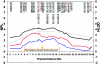
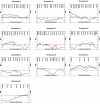
Previous linkage studies in schizophrenia have been discouraging due to inconsistent findings and weak signals. Genetic heterogeneity has been cited as one of the primary culprits for such inconsistencies. We have performed a 10-cM autosomal genomewide linkage scan for schizophrenia susceptibility regions, using 29 multiplex families of Ashkenazi Jewish descent. Although there is no evidence that the rate of schizophrenia among the Ashkenazim differs from that in other populations, we have focused on this population in hopes of reducing genetic heterogeneity among families and increasing the detectable effects of any particular locus. We pursued both allele-sharing and parametric linkage analyses as implemented in Genehunter, version 2.0. Our strongest signal was achieved at chromosome 10q22.3 (D10S1686), with a nonparametric linkage score (NPL) of 3.35 (genomewide empirical P=.035) and a dominant heterogeneity LOD score (HLOD) of 3.14. Six other regions gave NPL scores >2.00 (on chromosomes 1p32.2, 4q34.3, 6p21.31, 7p15.2, 15q11.2, and 21q21.2). Upon follow-up with an additional 23 markers in the chromosome 10q region, our peak NPL score increased to 4.27 (D10S1774; empirical P=.00002), with a 95% confidence interval of 12.2 Mb for the location of the trait locus (D10S1677 to D10S1753). We find these results encouraging for the study of schizophrenia among Ashkenazi families and suggest further linkage and association studies in this chromosome 10q region.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genomewide linkage scan for bipolar-disorder susceptibility loci among Ashkenazi Jewish families.Am J Hum Genet. 2004 Aug;75(2):204-19. doi: 10.1086/422474. Epub 2004 Jun 18. Am J Hum Genet. 2004. PMID: 15208783 Free PMC article.
-
Chromosome 10q harbors a susceptibility locus for bipolar disorder in Ashkenazi Jewish families.Mol Psychiatry. 2008 Apr;13(4):442-50. doi: 10.1038/sj.mp.4002039. Epub 2007 Jun 19. Mol Psychiatry. 2008. PMID: 17579605
-
Identification of a prostate cancer susceptibility locus on chromosome 7q11-21 in Jewish families.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Feb 17;101(7):1939-44. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0308336100. Epub 2004 Feb 9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. PMID: 14769943 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in the genetics of schizophrenia.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2002 Feb;59(2):331-48. doi: 10.1007/s00018-002-8426-6. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2002. PMID: 11915947 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Finding schizophrenia genes.J Clin Invest. 2005 Jun;115(6):1440-8. doi: 10.1172/JCI24759. J Clin Invest. 2005. PMID: 15931379 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genomewide linkage scan of schizophrenia in a large multicenter pedigree sample using single nucleotide polymorphisms.Mol Psychiatry. 2009 Aug;14(8):786-95. doi: 10.1038/mp.2009.11. Epub 2009 Feb 17. Mol Psychiatry. 2009. PMID: 19223858 Free PMC article.
-
Neuregulin 3 Knockout Mice Exhibit Behaviors Consistent with Psychotic Disorders.Mol Neuropsychiatry. 2016 Jul;2(2):79-87. doi: 10.1159/000445836. Epub 2016 May 20. Mol Neuropsychiatry. 2016. PMID: 27606322 Free PMC article.
-
Genomewide linkage scan for bipolar-disorder susceptibility loci among Ashkenazi Jewish families.Am J Hum Genet. 2004 Aug;75(2):204-19. doi: 10.1086/422474. Epub 2004 Jun 18. Am J Hum Genet. 2004. PMID: 15208783 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of neuregulin 3 genotype on human prefrontal cortex physiology.J Neurosci. 2014 Jan 15;34(3):1051-6. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3496-13.2014. J Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24431462 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Calcyon upregulation in adolescence impairs response inhibition and working memory in adulthood.Mol Psychiatry. 2011 Jun;16(6):672-84. doi: 10.1038/mp.2011.14. Epub 2011 Mar 15. Mol Psychiatry. 2011. PMID: 21403673 Free PMC article.
References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- Australian Genome Research Center, http://www.agrf.org.au
-
- CEPH-Généthon Integrated Map, http://www.cephb.fr/ceph-genethon-map.html
-
- Diagnostic Interview for Genetic Studies, http://zork.wustl.edu/nimh.digs/newpage11.htm
-
- Epidemiology-Genetics Program in Psychiatry, http://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/epigen
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim/ (for SZ and NRG1) - PubMed
References
-
- Abecasis GR, Cherny SS, Cookson WO, Cardon LR (2002) Merlin: apid analysis of dense genetic maps using sparse gene flow trees. Nat Genet 30: 97–101 - PubMed
-
- American Psychiatric Association (1994) Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 4th ed. American Psychiatric Association, Washington, DC
-
- Badner JA, Gershon ES (2002) Meta-analysis of whole-genome linkage scans of bipolar disorder and schizophrenia. Mol Psychiatry 7: 405–411 - PubMed
-
- Blouin JL, Dombroski BA, Nath SK, Lasseter VK, Wolyniec PS, Nestadt G, Thornquist M, et al (1998) Schizophrenia susceptibility loci on chromosomes 13q32 and 8p21. Nat Genet 20:70–73 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

