CD8beta/CD28 expression defines functionally distinct populations of peripheral blood T lymphocytes
- PMID: 12930358
- PMCID: PMC1808803
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2003.02226.x
CD8beta/CD28 expression defines functionally distinct populations of peripheral blood T lymphocytes
Abstract
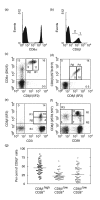
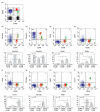
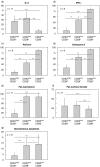
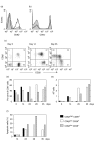
Peripheral blood CD8+ T lymphocytes generally express the CD8 coreceptor as an alphabeta heterodimer. On these cells, the CD8beta chain is present either at high (CD8betahigh) or low density (CD8betalow). CD8betahigh cells are CD28+, whereas CD8betalow cells are CD28+ or CD28-. Therefore, three subpopulations of CD8+ T cells can be described: (i) CD8betahighCD28+ (ii) CD8betalowCD28+, and (iii) CD8betalowCD28- cells. Phenotypic and functional characterization of these CD8+ T cell subsets revealed significant differences. CD8betahighCD28+ cells predominantly express CD45RA. In contrast, CD8betalowCD28+ cells frequently express CD45R0 and the activating NK receptor CD161. CD8betalowCD28- cells frequently revert to the CD45RA phenotype. In addition, these cells express CD16, CD56, CD94, and the killer-inhibitory receptors NKB1 and CD158a. Intracellular IL-2 was frequently detected in CD8betahighCD28+ cells and CD8betalowCD28+ cells, but not CD8betalowCD28- cells. CD8betalowCD28+ cells and CD8betalowCD28- cells frequently stained positive for IFN-gamma. In addition, these cells contain intracellular perforin and granzyme A. Expression of Fas (CD95) as well as susceptibility to apoptosis is markedly increased in CD8betalowCD28+ and CD8betalowCD28- cells as compared to CD8betahighCD28+ cells. In vitro activation of peripheral blood lymphocytes triggered expansion of CD8betahighCD28+ cells as well as a development into CD8betalowCD28+ and CD8betalowCD28- cells. Similarly, activation of CD8betahighCD28+ cord blood cells resulted in the appearance of CD8betalowCD28+ and CD8betalowCD28- cells. These data suggest that CD8betahighCD28+ cells can differentiate into CD8betalowCD28+ and CD8betalowCD28- cells upon TCR stimulation. Therefore, the CD8beta/CD28 subsets in peripheral blood may reflect distinct stages of post-thymic CD8+T cell development.
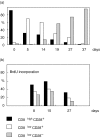
Figures
References
-
- Littman DR, Thomas Y, Maddon PJ, Chess L, Axel R. The isolation and sequence of the gene encoding T8: a molecule defining functional classes of T lymphocytes. Cell. 1985;40:237–46. - PubMed
-
- Liaw CW, Zamoyska R, Parnes JR. Structure, sequence, and polymorphism of the Lyt-2 T cell differentiation antigen gene. J Immunol. 1986;137:1037–43. - PubMed
-
- Renard V, Delon J, Luescher IF, Malissen B, Vivier E, Trautmann A. The CD8 beta polypeptide is required for the recognition of an altered peptide ligand as an agonist. Eur J Immunol. 1996;26:2999–3007. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

