Predictive markers for development of strongyloidiasis in patients infected with both Strongyloides stercoralis and HTLV-1
- PMID: 12930366
- PMCID: PMC1808792
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2003.02224.x
Predictive markers for development of strongyloidiasis in patients infected with both Strongyloides stercoralis and HTLV-1
Abstract
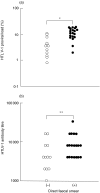
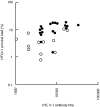
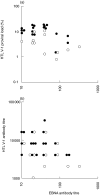
Severe strongyloidiasis has often been reported to occur in some patients infected with both Strongyloides stercoralis (S. stercoralis) and human T-cell leukaemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1); however, there are few useful predictive markers for the risk of development of strongyloidiasis in these patients. To search for such predictive markers, we examined peripheral blood and stool samples of individuals infected with both S. stercoralis and HTLV-1 in Okinawa, Japan, an area in which both of these are endemic. The HTLV-1 proviral load and antibody titre were examined in relation to the S. stercoralis load as measured by the direct faecal smear method in patients infected with both S. stercoralis and HTLV-1. The Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-associated nuclear antigen (EBNA) antibody titre was also measured in these patients in order to examine the relationship between host immunity and HTLV-1 proviral load or antibody titre. The direct faecal smear-positive group showed both a higher HTLV-1 proviral load and HTLV-1 antibody titre than the -negative group (P < 0.05). In contrast, inverse correlations of these parameters with the EBNA antibody titre were observed, especially for proviral load (rho = -0.387, P < 0.05). These results suggest that HTLV-1 proviral load and antibody titre influence the S. stercoralis load via disturbance of the host immunity, and that proviral load would be an especially useful predictive marker of the risk of development of strongyloidiasis in patients infected with both S. stercoralis and HTLV-1.
Figures
References
-
- Gessain A, Barin F, Vernant JC, Gout O, Maurs L, Calender A, de The G. Antibodies to human T lymphotropic virus type-I in patients with tropic spastic paraparesis. Lancet. 1985;2:407–10. - PubMed
-
- Osame M, Usuku K, Izumo S, Ijichi N, Amitani H, Igata A, Matsumoto M, Tara M. HTLV-I-associated myelopathy, a new clinical entity. Lancet. 1986;1:1031–2. - PubMed
-
- Mochizuki M, Yamaguchi K, Takatsuki K, Watanabe T, Mon S, Tajima K. HTLV-I and uveitis. Lancet. 1992;339:1110. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

