A small molecule HIV-1 inhibitor that targets the HIV-1 envelope and inhibits CD4 receptor binding
- PMID: 12930892
- PMCID: PMC196918
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1832214100
A small molecule HIV-1 inhibitor that targets the HIV-1 envelope and inhibits CD4 receptor binding
Abstract
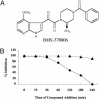
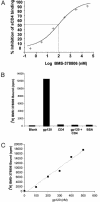
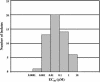
BMS-378806 is a recently discovered small molecule HIV-1 inhibitor that blocks viral entrance to cells. The compound exhibits potent inhibitory activity against a panel of R5-(virus using the CCR5 coreceptor), X4-(virus using the CXCR4 coreceptor), and R5/X4 HIV-1 laboratory and clinical isolates of the B subtype (median EC50 of 0.04 microM) in culture assays. BMS-378806 is selective for HIV-1 and inactive against HIV-2, SIV and a panel of other viruses, and exhibits no significant cytotoxicity in the 14 cell types tested (concentration for 50% reduction of cell growth, >225 microM). Mechanism of action studies demonstrated that BMS-378806 binds to gp120 and inhibits the interactions of the HIV-1 envelope protein to cellular CD4 receptors. Further confirmation that BMS-378806 targets the envelope in infected cells was obtained through the isolation of resistant variants and the mapping of resistance substitutions to the HIV-1 envelope. In particular, two substitutions, M426L and M475I, are situated in the CD4 binding pocket of gp120. Recombinant HIV-1 carrying these two substitutions demonstrated significantly reduced susceptibility to compound inhibition. BMS-378806 displays many favorable pharmacological traits, such as low protein binding, minimal human serum effect on anti-HIV-1 potency, good oral bioavailability in animal species, and a clean safety profile in initial animal toxicology studies. Together, the data show that BMS-378806 is a representative of a new class of HIV inhibitors that has the potential to become a valued addition to our current armamentarium of antiretroviral drugs.
Figures
Comment in
-
Blocking the docking of HIV-1.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Sep 16;100(19):10581-2. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2035071100. Epub 2003 Sep 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003. PMID: 12963807 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Cohen, O. J. & Fauci, A. S. (2001) Adv. Intern. Med. 46, 207–246. - PubMed
-
- Volberding, P. (1999) AIDS 13, S1–S9. - PubMed
-
- Wegner, S. A., Brodine, S. K., Mascola, J. R., Tasker, S. A., Shaffer, R. A., Starkey, M. J., Barile, A., Martin, G. J., Aronson, N., Emmons, W. W., et al. (2000) AIDS 14, 1009–1015. - PubMed
-
- Little, S. J., Holte, S., Routy, J. P., Daar, E., Markowitz, M., Collier, A. C., Koup, R. A., Mellors, J. W., Connick, E., Conway, B., et al. (2002) N. Engl. J. Med. 347, 385–394. - PubMed
-
- LaBranche, C. C., Galasso, G., Moore, J. P., Bolognesi, D., Hirsch, M. S. & Hammer, S. M. (2001) Antiviral Res. 50, 95–115. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

