Increase in signal-to-noise ratio of > 10,000 times in liquid-state NMR
- PMID: 12930897
- PMCID: PMC193532
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1733835100
Increase in signal-to-noise ratio of > 10,000 times in liquid-state NMR
Abstract
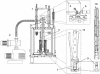
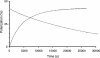
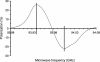
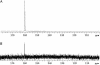
A method for obtaining strongly polarized nuclear spins in solution has been developed. The method uses low temperature, high magnetic field, and dynamic nuclear polarization (DNP) to strongly polarize nuclear spins in the solid state. The solid sample is subsequently dissolved rapidly in a suitable solvent to create a solution of molecules with hyperpolarized nuclear spins. The polarization is performed in a DNP polarizer, consisting of a super-conducting magnet (3.35 T) and a liquid-helium cooled sample space. The sample is irradiated with microwaves at approximately 94 GHz. Subsequent to polarization, the sample is dissolved by an injection system inside the DNP magnet. The dissolution process effectively preserves the nuclear polarization. The resulting hyperpolarized liquid sample can be transferred to a high-resolution NMR spectrometer, where an enhanced NMR signal can be acquired, or it may be used as an agent for in vivo imaging or spectroscopy. In this article we describe the use of the method on aqueous solutions of [13C]urea. Polarizations of 37% for 13C and 7.8% for 15N, respectively, were obtained after the dissolution. These polarizations correspond to an enhancement of 44,400 for 13C and 23,500 for 15N, respectively, compared with thermal equilibrium at 9.4 T and room temperature. The method can be used generally for signal enhancement and reduction of measurement time in liquid-state NMR and opens up for a variety of in vitro and in vivo applications of DNP-enhanced NMR.
Figures

References
-
- Brossel, J. & Kastler, A. (1949) La Détection de la Résonance Magnétique des Niveaux Excités: l'Effet de Dépolarisation des Radiations de Résonance Optique et de Fluorescence 229, 1213-1215.
-
- Golman, K., Axelsson, O., Jóhannesson, H., Månsson, S., Olofsson, C. & Petersson, J. S. (2001) Magn. Reson. Med. 46, 1-5. - PubMed
-
- Haake, M., Natterer, J. & Bargon, J. (1996) J. Am. Chem. Soc. 118, 8688-8691.
-
- Abragam, A. & Goldman, M. (1978) Rep. Prog. Phys. 41, 395-467.
-
- Goldman, M. (1970) Spin Temperature and Nuclear Magnetic Resonance in Solids (Oxford Univ. Press, Oxford).
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

