Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP-1) has a controlling role in homologous recombination
- PMID: 12930944
- PMCID: PMC212803
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkg703
Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP-1) has a controlling role in homologous recombination
Abstract
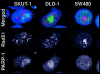
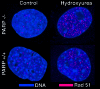
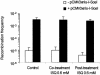
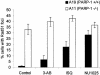
Cells with non-functional poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP-1) show increased levels of sister chromatid exchange, suggesting a hyper recombination phenotype in these cells. To further investigate the involvement of PARP-1 in homologous recombination (HR) we investigated how PARP-1 affects nuclear HR sites (Rad51 foci) and HR repair of an endonuclease-induced DNA double-strand break (DSB). Several proteins involved in HR localise to Rad51 foci and HR-deficient cells fail to form Rad51 foci in response to DNA damage. Here, we show that PARP-1 mainly does not localise to Rad51 foci and that Rad51 foci form in PARP-1-/- cells, also in response to hydroxyurea. Furthermore, we show that homology directed repair following induction of a site-specific DSB is normal in PARP-1-inhibited cells. In contrast, inhibition or loss of PARP-1 increases spontaneous Rad51 foci formation, confirming a hyper recombination phenotype in these cells. Our data suggest that PARP-1 controls DNA damage recognised by HR and that it is not involved in executing HR as such.
Figures

References
-
- Herceg Z. and Wang,Z.Q. (2001) Functions of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) in DNA repair, genomic integrity and cell death. Mutat. Res., 477, 97–110. - PubMed
-
- Satoh M.S. and Lindahl,T. (1992) Role of poly(ADP-ribose) formation in DNA repair. Nature, 356, 356–358. - PubMed
-
- Lindahl T., Satoh,M.S., Poirier,G.G. and Klungland,A. (1995) Post-translational modification of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase induced by DNA strand breaks. Trends Biochem. Sci., 20, 405–411. - PubMed
-
- Shall S. and de Murcia,G. (2000) Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1: what have we learned from the deficient mouse model? Mutat. Res., 460, 1–15. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

