Developmental defects by antisense-mediated inactivation of micro-RNAs 2 and 13 in Drosophila and the identification of putative target genes
- PMID: 12930946
- PMCID: PMC212806
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkg707
Developmental defects by antisense-mediated inactivation of micro-RNAs 2 and 13 in Drosophila and the identification of putative target genes
Abstract
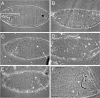
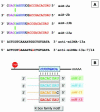
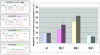
Micro-RNAs are a class of small non-coding regulatory RNAs that impair translation by imperfect base pairing to mRNAs. For analysis of their cellular function we injected different miRNA-specific DNA antisense oligonucleotides in Drosophila embryos. In four cases we observed severe interference with normal development, one had a moderate impact and six oligonucleotides did not cause detectable phenotypes. We further used the miR-13a DNA antisense oligonucleotide as a PCR primer on a cDNA library template. In this experimental way we identified nine Drosophila genes, which are characterised by 3' untranslated region motifs that allow imperfect duplex formation with miR-13 or related miRNAs. These genes, which include Sos and Myd88, represent putative targets for miRNA regulation. Mutagenesis of the target motif of two genes followed by transfection in Drosophila Schneider 2 (S2) cells and subsequent reporter gene analysis confirmed the hypothesis that the binding potential of miR-13 is inversely correlated with gene expression.
Figures

References
-
- Lagos-Quintana M., Rauhut,R., Lendeckel,W. and Tuschl,T. (2001) Identification of novel genes coding for small expressed RNAs. Science, 294, 853–858. - PubMed
-
- Lau N.C., Lim,L.P., Weinstein,E.G. and Bartel,D.P. (2001) An abundant class of tiny RNAs with probable regulatory roles in Caenorhabditis elegans. Science, 294, 858–62. - PubMed
-
- Lee R.C. and Ambros,V. (2001) An extensive class of small RNAs in Caenorhabditis elegans. Science, 294, 862–864. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

