Promoter choice affects the potency of HIV-1 specific RNA interference
- PMID: 12930953
- PMCID: PMC212804
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkg704
Promoter choice affects the potency of HIV-1 specific RNA interference
Abstract
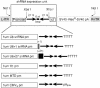
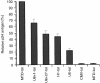
RNA interference (RNAi) is mediated by small interfering (si) RNAs that target and degrade mRNA in a sequence-specific manner. Cellular expression of siRNA can be achieved by the use of expression cassettes driven by RNA polymerase III (pol III) promoters. Here, we demonstrate that a modified tRNA(met)-derived (MTD) promoter effectively drives the cellular expression of HIV-1-specific siRNA. We observed up to 56% greater inhibition of virus production when the MTD promoter was used to drive the expression of short hairpin (sh) RNA targeting the HIV-1 transactivator protein tat compared to cassettes containing other pol III promoters such as H1, U6+1 and U6+27. We conclude that the MTD promoter is ideally suited to drive intracellular expression of HIV-1 specific siRNA and may serve as an important component of future RNAi vector delivery systems.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 escape from RNA interference.J Virol. 2003 Nov;77(21):11531-5. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.21.11531-11535.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 14557638 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced gene silencing of HIV-1 specific siRNA using microRNA designed hairpins.Nucleic Acids Res. 2004 Feb 13;32(3):1154-8. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkh278. Print 2004. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004. PMID: 14966264 Free PMC article.
-
Efficient gene transfer of HIV-1-specific short hairpin RNA into human lymphocytic cells using recombinant adeno-associated virus vectors.Mol Ther. 2004 Mar;9(3):396-402. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2003.11.025. Mol Ther. 2004. PMID: 15006606
-
HIV-1-specific RNA interference.Curr Opin Mol Ther. 2004 Aug;6(4):373-80. Curr Opin Mol Ther. 2004. PMID: 15468596 Review.
-
RNAi as a treatment for HIV-1 infection.Biotechniques. 2006 Apr;Suppl:25-9. doi: 10.2144/000112167. Biotechniques. 2006. PMID: 16629384 Review.
Cited by
-
Effective suppression of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 through a combination of short- or long-hairpin RNAs targeting essential sequences for retroviral integration.J Virol. 2006 Aug;80(15):7658-66. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00078-06. J Virol. 2006. PMID: 16840344 Free PMC article.
-
A hybrid CMV-H1 construct improves efficiency of PEI-delivered shRNA in the mouse brain.Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35(9):e65. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm152. Epub 2007 Apr 10. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007. PMID: 17426128 Free PMC article.
-
Are microRNAs Important Players in HIV-1 Infection? An Update.Viruses. 2018 Mar 3;10(3):110. doi: 10.3390/v10030110. Viruses. 2018. PMID: 29510515 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA interference: its use as antiviral therapy.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2006;173(173):117-50. doi: 10.1007/3-540-27262-3_7. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16594614 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Toward a durable anti-HIV gene therapy based on RNA interference.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2009 Sep;1175(1):3-14. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2009.04972.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2009. PMID: 19796072 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lee N.S., Dohjima,T., Bauer,G., Li,H., Li,M.J., Ehsani,A., Salvaterra,P. and Rossi,J. (2002) Expression of small interfering RNAs targeted against HIV-1 rev transcripts in human cells. Nat. Biotechnol., 20, 500–505. - PubMed
-
- Brummelkamp T.R., Bernards,R. and Agami,R. (2002) Stable suppression of tumorigenicity by virus-mediated RNA interference. Cancer Cells, 2, 243–247. - PubMed
-
- Paul C.P., Good,P.D., Winer,I. and Engelke,D.R. (2002) Effective expression of small interfering RNA in human cells. Nat. Biotechnol., 20, 505–508. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

