mRNA fusion constructs serve in a general cell-based assay to profile oligonucleotide activity
- PMID: 12930976
- PMCID: PMC212822
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gng103
mRNA fusion constructs serve in a general cell-based assay to profile oligonucleotide activity
Abstract
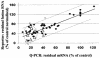
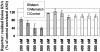
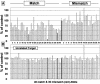
A cellular assay has been developed to allow measurement of the inhibitory activity of large numbers of oligonucleotides at the protein level. The assay is centred on an mRNA fusion transcript construct comprising of a full-length reporter gene with a target region of interest inserted into the 3'-untranslated region. Luciferase and fluorescent reporter genes were used in the constructs. The insert can be from multiple sources (uncharacterised ESTs, partial or full-length genes, genes from alternate species, etc.). Large numbers of oligonucleotides were screened for antisense activity against a number of such constructs bearing different reporters, in different cell lines and the inhibitory profiles obtained were compared with those observed through screening the oligonucleotides against the corresponding endogenous genes assayed at the mRNA level. A high degree of similarity in the profiles was obtained indicating that the fusion constructs are suitable surrogates for the endogenous messages for characterisation of antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs). Furthermore, the results support the hypothesis that the secondary structure of mRNAs are divided into domains, the nature of which is determined by primary nucleotide sequence. Oligonucleotides whose activity is dependent on the local structure of their target mRNAs (e.g. ASOs, short interfering RNAs) can be characterised via such fusion RNA constructs.
Figures



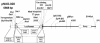
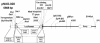
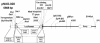

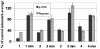
References
-
- Bennett C.F. and Cowsert,L.M. (1999) Application of antisense oligonucleotides for gene functionalization and target validation. Curr. Opin. Mol. Ther., 1, 359–371. - PubMed
-
- Taylor M.F., Wiederholt,K. and Sverdrup,F. (1999) Antisense oligonucleotides: a systematic high-throughput approach to target validation and gene function determination. Drug Discovery Today, 4, 562–567. - PubMed
-
- Thompson J.D. (2002) Applications of antisense and siRNAs during preclinical drug development. Drug Discovery Today, 7, 912–916. - PubMed
-
- Golden T., Dean,N.M. and Honkanen,R.E. (2002) Use of antisense oligonucleotides: advantages, controls and cardiovascular tissue. Microcirculation, 9, 51–64. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

