Solution structure of Pi4, a short four-disulfide-bridged scorpion toxin specific of potassium channels
- PMID: 12930984
- PMCID: PMC2323982
- DOI: 10.1110/ps.03186703
Solution structure of Pi4, a short four-disulfide-bridged scorpion toxin specific of potassium channels
Erratum in
- Protein Sci. 2003 Nov;12(11):2650. Possani Lourrival D [corrected to Possani Lourival D]
Abstract
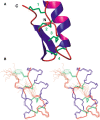
Pi4 is a short toxin found at very low abundance in the venom of Pandinus imperator scorpions. It is a potent blocker of K(+) channels. Like the other members of the alpha-KTX6 subfamily to which it belongs, it is cross-linked by four disulfide bonds. The synthetic analog (sPi4) and the natural toxin (nPi4) have been obtained by solid-phase synthesis or from scorpion venom, respectively. Analysis of two-dimensional (1)H NMR spectra of nPi4 and sPi4 indicates that both peptides have the same structure. Moreover, electrophysiological recordings of the blocking of Shaker B K(+) channels by sPi4 (K(D) = 8.5 nM) indicate that sPi4 has the same blocking activity of nPi4 (K(D) = 8.0 nM), previously described. The disulfide bonds have been independently determined by NMR and structure calculations, and by Edman-degradation/mass-spectrometry identification of peptides obtained by proteolysis of nPi4. Both approaches indicate that the pairing of the half-cystines is (6)C-(27)C, (12)C-(32)C, (16)C-(34)C, and (22)C-(37)C. The structure of the toxin has been determined by using 705 constraints derived from NMR data on sPi4. The structure, which is well defined, shows the characteristic alpha/beta scaffold of scorpion toxins. It is compared to the structure of the other alpha-KTX6 subfamily members and, in particular, to the structure of maurotoxin, which shows a different pattern of disulfide bridges despite its high degree of sequence identity (76%) with Pi4. The structure of Pi4 and the high amounts of synthetic peptide available, will enable the detailed analysis of the interaction of Pi4 with K(+) channels.
Figures




References
-
- Batista, C.V.F., Gómez-Lagunas, F., Lucas, S., and Possani, L.D. 2000. Tc1, from Tityus cambridgei, is the first member of a new subfamily of scorpion toxins that blocks K+-channels. FEBS Lett. 486 117–120. - PubMed
-
- Bax, A. and Davis, D.G. 1985. MLEV-17–based two-dimensional homonuclear magnetization transfer spectroscopy. J. Magn. Reson. 65 355–360.
-
- Blanc, E., Sabatier, J.M., Kharrat, R., Meunier, S., El Ayeb, M., Van Rietschoten, J., and Darbon, H. 1997. Solution structure of maurotoxin, a scorpion toxin from Scorpio maurus, with high affinity for voltage-gated potassium channels. Protein 29 321–333. - PubMed
-
- Boisbouvier, J., Blackledge, M., Sollier, A., and Marion, D. 2000. Simultaneous determination of disulphide bridge topology and three-dimensional structure using ambiguous intersulphur distance restraints: Possibilities and limitations. J. Biomol. NMR 16 197–208. - PubMed
-
- Bontems, F., Roumestand, C., Gilquin, B., Ménez, A., and Toma, F. 1991. Refined structure of charybdotoxin: Common motifs in scorpion toxins and insects defensins. Science 253 1521–1523. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

