The triterpenoid CDDO inhibits expression of matrix metalloproteinase-1, matrix metalloproteinase-13 and Bcl-3 in primary human chondrocytes
- PMID: 12932292
- PMCID: PMC193729
- DOI: 10.1186/ar792
The triterpenoid CDDO inhibits expression of matrix metalloproteinase-1, matrix metalloproteinase-13 and Bcl-3 in primary human chondrocytes
Abstract
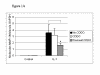
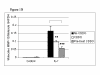
A synthetic triterpenoid, 2-cyano-3,12-dioxoolean-1,9-dien-28-oic acid (CDDO), has been reported to have anti-inflammatory properties and to decrease the interleukin-1 (IL-1)-induced expression of matrix metalloproteinase-1 (MMP-1) and MMP-13. We have shown previously that IL-1 induces expression of the inhibitor of NF-kappaB (IkappaB) family member Bcl-3, and that this contributes to MMP-1 expression. To quantify the effects of CDDO on IL-1-induced MMP-1, MMP-13 and Bcl-3 expression, we stimulated the chondrosarcoma cell line SW-1353 and human primary chondrocytes with IL-1, in the presence or absence of CDDO. Harvested RNA was subjected to quantitative real-time reverse-transcriptase polymerase chain reaction. In SW-1353 cells, 300 nM CDDO significantly decreased the induction of MMP-1 and MMP-13 by IL-1. In human primary chondrocytes, 300 nM CDDO inhibited the induction of these genes by IL-1 to an even greater extent. In both cell types, inhibition of MMP-1 required 24 hours of pretreatment with CDDO, whereas MMP-13 could be inhibited when CDDO and IL-1 were added simultaneously to culture. In human primary chondrocytes, IL-1-induced Bcl-3 expression was inhibited when cells were pretreated with CDDO. To determine whether the inhibitory effect of CDDO on MMP worked through inhibition of Bcl-3 gene expression, SW-1353 cells stably transfected with a Bcl-3 expression plasmid were treated with IL-1 and/or CDDO, and MMP gene expression was assayed. Overexpression of Bcl-3 increased MMP-1, but not MMP-13, mRNA levels. Furthermore, overexpressed Bcl-3 could sustain the CDDO-dependent inhibition of IL-1-induced MMP-1 expression. Our data demonstrate that CDDO inhibits IL-1-induced MMP-1 and MMP-13 expression in human chondrocytes. CDDO also inhibits the expression of Bcl-3, an IL-1-responsive gene that preferentially contributes to MMP-1 gene expression.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Bcl-3 is an interleukin-1-responsive gene in chondrocytes and synovial fibroblasts that activates transcription of the matrix metalloproteinase 1 gene.Arthritis Rheum. 2002 Dec;46(12):3230-9. doi: 10.1002/art.10675. Arthritis Rheum. 2002. PMID: 12483727
-
A synthetic triterpenoid selectively inhibits the induction of matrix metalloproteinases 1 and 13 by inflammatory cytokines.Arthritis Rheum. 2001 May;44(5):1096-104. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200105)44:5<1096::AID-ANR190>3.0.CO;2-6. Arthritis Rheum. 2001. PMID: 11352241
-
Matrix metalloproteinase 10 promotion of collagenolysis via procollagenase activation: implications for cartilage degradation in arthritis.Arthritis Rheum. 2006 Oct;54(10):3244-53. doi: 10.1002/art.22167. Arthritis Rheum. 2006. PMID: 17009259
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma-independent repression of collagenase gene expression by 2-cyano-3,12-dioxooleana-1,9-dien-28-oic acid and prostaglandin 15-deoxy-delta(12,14) J2: a role for Smad signaling.Mol Pharmacol. 2004 Feb;65(2):309-18. doi: 10.1124/mol.65.2.309. Mol Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 14742672
-
Inhibition of matrix metalloproteinase-1 by dichloromethylene bisphosphonate (clodronate).Calcif Tissue Int. 1997 Jul;61(1):59-61. doi: 10.1007/s002239900295. Calcif Tissue Int. 1997. PMID: 9192515 Review.
Cited by
-
A computer simulation approach to assessing therapeutic intervention points for the prevention of cytokine-induced cartilage breakdown.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014 Apr;66(4):979-89. doi: 10.1002/art.38297. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014. PMID: 24757149 Free PMC article.
-
IFNγ induces Bcl3 expression by JAK1/STAT1/p65 signaling, resulting in increased IL-8 expression in ovarian cancer cells.FEBS Open Bio. 2023 Aug;13(8):1495-1506. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.13624. Epub 2023 Jul 18. FEBS Open Bio. 2023. PMID: 37151134 Free PMC article.
-
RelA is required for IL-1beta stimulation of Matrix Metalloproteinase-1 expression in chondrocytes.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2007 Apr;15(4):431-41. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2006.09.011. Epub 2006 Nov 13. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2007. PMID: 17097317 Free PMC article.
-
COL2A1 and Caspase-3 as Promising Biomarkers for Osteoarthritis Prognosis in an Equus asinus Model.Biomolecules. 2020 Feb 26;10(3):354. doi: 10.3390/biom10030354. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32111016 Free PMC article.
-
Synthetic oleanane triterpenoids: multifunctional drugs with a broad range of applications for prevention and treatment of chronic disease.Pharmacol Rev. 2012 Oct;64(4):972-1003. doi: 10.1124/pr.111.004846. Epub 2012 Sep 10. Pharmacol Rev. 2012. PMID: 22966038 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Muir H. The chondrocyte, architect of cartilage. Biomechanics, structure, function and molecular biology of cartilage matrix macromolecules. BioEssays. 1995;17:1039–1048. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

