Calcium in plants
- PMID: 12933363
- PMCID: PMC4243668
- DOI: 10.1093/aob/mcg164
Calcium in plants
Abstract
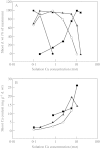
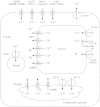
Calcium is an essential plant nutrient. It is required for various structural roles in the cell wall and membranes, it is a counter-cation for inorganic and organic anions in the vacuole, and the cytosolic Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]cyt) is an obligate intracellular messenger coordinating responses to numerous developmental cues and environmental challenges. This article provides an overview of the nutritional requirements of different plants for Ca, and how this impacts on natural flora and the Ca content of crops. It also reviews recent work on (a) the mechanisms of Ca2+ transport across cellular membranes, (b) understanding the origins and specificity of [Ca2+]cyt signals and (c) characterizing the cellular [Ca2+]cyt-sensors (such as calmodulin, calcineurin B-like proteins and calcium-dependent protein kinases) that allow plant cells to respond appropriately to [Ca2+]cyt signals.
Figures


References
-
- AcheP, Becker D, Ivashikina N, Dietrich P, Roelfsema MRG, Hedrich R.2000. GORK, a delayed outward rectifier expressed in guard cells of Arabidopsis thaliana, is a K+‐selective, K+‐sensing ion channel. FEBS Letters 486: 93–98. - PubMed
-
- AllenGJ, Sanders D.1997. Vacuolar ion channels in higher plants. Advances in Botanical Research 25: 217–252.
-
- AllenGJ, Chu SP, Harrington CL, Schumacher K, Hoffmann T, Tang YY, Grill E, Schroeder JI.2001. A defined range of guard cell calcium oscillation parameters encodes stomatal movements. Nature 411: 1053–1057. - PubMed
-
- AllenGJ, Chu SP, Schumacher K, Shimazaki CT, Vafeados D, Kemper A, Hawke SD, Tallman G, Tsien RY, Harper JF et al.2000. Alteration of stimulus specific guard cell calcium oscillations and stomatal closing in Arabidopsis det3 mutant. Science 289: 2338–2342. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

