Multiple elements controlling adherence of enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7 to HeLa cells
- PMID: 12933841
- PMCID: PMC187298
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.71.9.4985-4995.2003
Multiple elements controlling adherence of enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7 to HeLa cells
Abstract
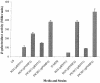
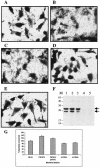
Adherence of enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli (EHEC) to the intestinal epithelium is essential for initiation of infection. Intimin is the only factor demonstrated to play a role in intestinal colonization by EHEC O157:H7. Other attempts to identify additional adhesion factors in vitro have been unsuccessful, suggesting that expression of these factors is under tight regulation. We sought to identify genes involved in the control of adherence of EHEC O157:H7 to cultured epithelial cells. A total of 5,000 independent transposon insertion mutants were screened for their ability to adhere to HeLa cells, and 7 mutants were isolated with a markedly enhanced adherence. The mutants adhered at levels 113 to 170% that of the wild-type strain, and analysis of the protein profiles of these mutants revealed several proteins differentially expressed under in vitro culture conditions. We determined the sequence of the differentially expressed proteins and further investigated the function of OmpA, whose expression was increased in a mutant with an insertionally inactivated tcdA gene. An isogenic ompA mutant showed reduced adherence compared to the parent strain. Disruption of the ompA gene in the tdcA mutant strain abolished the hyperadherent phenotype, and anti-OmpA serum inhibited adhesion of wild-type and tdcA mutant strains to HeLa cells. Enhanced adhesion mediated by OmpA was also observed with Caco-2 cells, and anti-OmpA serum blocked adherence to HeLa cells of other EHEC O157:H7 strains. Our results indicate that multiple elements control adherence and OmpA acts as an adhesin in EHEC O157:H7.
Figures



Similar articles
-
CadA negatively regulates Escherichia coli O157:H7 adherence and intestinal colonization.Infect Immun. 2008 Nov;76(11):5072-81. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00677-08. Epub 2008 Sep 15. Infect Immun. 2008. PMID: 18794292 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation and characterization of mini-Tn5Km2 insertion mutants of enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7 deficient in adherence to Caco-2 cells.Infect Immun. 2000 Oct;68(10):5943-52. doi: 10.1128/IAI.68.10.5943-5952.2000. Infect Immun. 2000. PMID: 10992506 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and characterization of lpfABCC'DE, a fimbrial operon of enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7.Infect Immun. 2002 Oct;70(10):5416-27. doi: 10.1128/IAI.70.10.5416-5427.2002. Infect Immun. 2002. PMID: 12228266 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of the Ler- and H-NS-regulated long polar fimbriae of Escherichia coli O157:H7 during binding to tissue-cultured cells.Infect Immun. 2008 Nov;76(11):5062-71. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00654-08. Epub 2008 Sep 15. Infect Immun. 2008. PMID: 18794291 Free PMC article.
-
Fimbriation and curliation in Escherichia coli O157:H7: a paradigm of intestinal and environmental colonization.Gut Microbes. 2012 May-Jun;3(3):272-6. doi: 10.4161/gmic.20661. Epub 2012 May 1. Gut Microbes. 2012. PMID: 22614704 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Advances in the development of enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli vaccines using murine models of infection.Vaccine. 2013 Jul 11;31(32):3229-35. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2013.05.013. Epub 2013 May 22. Vaccine. 2013. PMID: 23707170 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role for flagella but not intimin in the persistent infection of the gastrointestinal tissues of specific-pathogen-free chicks by shiga toxin-negative Escherichia coli O157:H7.Infect Immun. 2005 Mar;73(3):1836-46. doi: 10.1128/IAI.73.3.1836-1846.2005. Infect Immun. 2005. PMID: 15731085 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of OmpA in Type III Secretion System-Mediated Virulence of Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli.Pathogens. 2021 Nov 17;10(11):1496. doi: 10.3390/pathogens10111496. Pathogens. 2021. PMID: 34832651 Free PMC article.
-
CadA negatively regulates Escherichia coli O157:H7 adherence and intestinal colonization.Infect Immun. 2008 Nov;76(11):5072-81. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00677-08. Epub 2008 Sep 15. Infect Immun. 2008. PMID: 18794292 Free PMC article.
-
In-silico design, expression, and purification of novel chimeric Escherichia coli O157:H7 OmpA fused to LTB protein in Escherichia coli.PLoS One. 2017 Mar 15;12(3):e0173761. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0173761. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28296951 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

