A novel pathogenicity island integrated adjacent to the thrW tRNA gene of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli encodes a vacuolating autotransporter toxin
- PMID: 12933851
- PMCID: PMC187369
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.71.9.5087-5096.2003
A novel pathogenicity island integrated adjacent to the thrW tRNA gene of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli encodes a vacuolating autotransporter toxin
Abstract
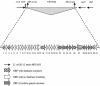
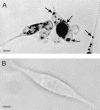
We report the complete nucleotide sequence and genetic organization of the Vat-encoding pathogenicity island (PAI) of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli strain Ec222. The 22,139-bp PAI is situated adjacent to the 3' terminus of the thrW tRNA gene, has a G+C content of 41.2%, and includes a bacteriophage SfII integrase gene, mobile genetic elements, two open reading frames with products exhibiting sequence similarity to known proteins, and several other open reading frames of unknown function. The PAI encodes an autotransporter protein, Vat (vacuolating autotransporter toxin), which induces the formation of intracellular vacuoles resulting in cytotoxic effects similar to those caused by the VacA toxin from Helicobacter pylori. The predicted 148.3-kDa protein product possesses the three domains that are typical of serine protease autotransporters of Enterobacteriaceae: an N-terminal signal sequence of 55 amino acids, a 111.8-kDa passenger domain containing a modified serine protease site (ATSGSG), and a C-terminal outer membrane translocator of 30.5 kDa. Vat has 75% protein homology with the hemagglutinin Tsh, an autotransporter of avian pathogenic E. coli. A vat deletion mutant of Ec222 showed no virulence in respiratory and cellulitis infection models of disease in broiler chickens. We conclude that the newly described PAI and Vat may be involved in the pathogenicity of avian septicemic E. coli strain Ec222 and other avian pathogenic E. coli strains.
Figures
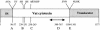



Similar articles
-
Identification and molecular characterization of EatA, an autotransporter protein of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli.Infect Immun. 2004 Mar;72(3):1786-94. doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.3.1786-1794.2004. Infect Immun. 2004. PMID: 14977988 Free PMC article.
-
[Vacuolating autotransporter toxin affects biological characteristics and pathogenicity of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli].Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao. 2015 Sep 4;55(9):1208-14. Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao. 2015. PMID: 26762034 Chinese.
-
Identification of sat, an autotransporter toxin produced by uropathogenic Escherichia coli.Mol Microbiol. 2000 Oct;38(1):53-66. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2000.02110.x. Mol Microbiol. 2000. PMID: 11029690
-
Regulation and function of Ag43 (flu).Annu Rev Microbiol. 2008;62:153-69. doi: 10.1146/annurev.micro.62.081307.162938. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18785838 Review.
-
Serine protease autotransporters of enterobacteriaceae (SPATEs): biogenesis and function.Toxins (Basel). 2010 Jun;2(6):1179-206. doi: 10.3390/toxins2061179. Epub 2010 May 28. Toxins (Basel). 2010. PMID: 22069633 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Distribution of the serine protease autotransporters of the Enterobacteriaceae among extraintestinal clinical isolates of Escherichia coli.J Clin Microbiol. 2005 Aug;43(8):4076-82. doi: 10.1128/JCM.43.8.4076-4082.2005. J Clin Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 16081954 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression subtractive hybridization identifies an autotransporter adhesin gene of E. coli IMT5155 specifically associated with avian pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC).BMC Microbiol. 2010 Sep 9;10:236. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-10-236. BMC Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20828376 Free PMC article.
-
Virulence Factors and Antimicrobial Resistance Profile of Escherichia Coli Isolated from Laying Hens in Italy.Animals (Basel). 2022 Jul 15;12(14):1812. doi: 10.3390/ani12141812. Animals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35883359 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization and functional analysis of AatB, a novel autotransporter adhesin and virulence factor of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli.Infect Immun. 2013 Jul;81(7):2437-47. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00102-13. Epub 2013 Apr 29. Infect Immun. 2013. PMID: 23630958 Free PMC article.
-
Pathotyping avian pathogenic Escherichia coli strains in Korea.J Vet Sci. 2012 Jun;13(2):145-52. doi: 10.4142/jvs.2012.13.2.145. J Vet Sci. 2012. PMID: 22705736 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Al-Hasani, K., I. R. Henderson, H. Sakellaris, K. Rajakumar, T. Grant, J. P. Nataro, R. Robins-Browne, and B. Adler. 2000. The sigA gene which is borne on the she pathogenicity island of Shigella flexneri 2a encodes an exported cytopathic protease involved in intestinal fluid accumulation. Infect. Immun. 68:2457-2463. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Benjelloun-Touimi, Z., M. S. Tahar, C. Montecucco, P. J. Sansonetti, and C. Parsot. 1998. SepA, the 110 kDa protein secreted by Shigella flexneri: two-domain structure and proteolytic activity. Microbiology 144:1815-1822. - PubMed
-
- Brunder, W., H. Schmidt, and H. Karch. 1997. EspP, a novel extracellular serine protease of enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7 cleaves human coagulation factor V. Mol. Microbiol. 24:767-778. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

