Binding of shiga toxin 2e to porcine erythrocytes in vivo and in vitro
- PMID: 12933864
- PMCID: PMC187359
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.71.9.5194-5201.2003
Binding of shiga toxin 2e to porcine erythrocytes in vivo and in vitro
Abstract
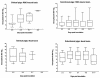
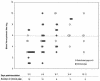
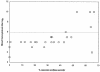
Shiga toxin 2e (Stx2e), produced by host-adapted Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli (STEC) strains, causes edema disease in weaned pigs. Edema disease is manifested as vascular necrosis, edema, neurologic signs, and death. In this study we sought to determine the correlation between the presence of Stx2e in the blood of STEC-inoculated pigs and the disease outcome. Eleven of 15 (73%) pigs with clinical and 5 of 35 (14%) pigs with subclinical edema disease had detectable levels of Stx2e in the red-blood-cell (RBC) fraction of their blood but not in serum or plasma. The presence of Stx2e in the RBC fraction was strongly associated with the development of clinical disease (relative risk, 5.8; P < 0.0001). Subclinical pigs with Stx2e in their blood developed more-extensive vascular lesions than pigs without detectable Stx2e in their blood (average proportions of necrotic arterioles, 63 and 27.5%, respectively; P = 0.001). Variations in RBC-bound Stx2e levels could in part reflect variations in the binding capacity of RBCs. As an initial step toward addressing this possibility, assays were conducted to determine if pigs vary in the Stx2e binding capacity of their RBCs. An in vitro study of noninoculated pigs demonstrated two phenotypes based on the capacity of the RBCs to bind Stx2e. While RBCs from most of the pigs consistently bound high levels of Stx2e (high-binding phenotype), consistently low Stx2e binding was detected in RBCs from a few pigs (low-binding phenotype). The low- and high-binding phenotypes of individual pigs remained consistent throughout repeated samplings over 2 months.
Figures

References
-
- Acheson, D. W., L. L. Lincicome, M. Jacewicz, and G. T. Keusch. 1998. Shiga toxin interaction with intestinal epithelial cells, p. 140-147. In J. B. Kaper and A. D. O'Brien (ed.), Escherichia coli O157:H7 and other Shiga toxin-producing E. coli strains. ASM Press, Washington, D.C.
-
- Ashida, A., K. Matsui, T. Chizaki, K. Yoshikawa, N. Kawamura, K. Suzuki, and H. Tamai. 1999. Erythrocyte P1 group antigen expression in VTEC-associated hemolytic uremic syndrome. Clin. Nephrol. 51:73-76. - PubMed
-
- Bertschinger, H. U., and C. L. Gyles. 1994. Oedema disease of pigs, p. 193-219. In C. L. Gyles (ed.), Escherichia coli in domestic animals and humans. CAB International, Wallingford, Conn.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

