The small nucleoid-binding proteins H-NS, HU, and Fis affect hilA expression in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium
- PMID: 12933899
- PMCID: PMC187364
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.71.9.5432-5435.2003
The small nucleoid-binding proteins H-NS, HU, and Fis affect hilA expression in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium
Abstract
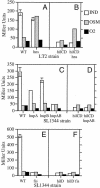
hilA encodes an activator of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium virulence genes and is transcriptionally modulated by environmental conditions. We show that H-NS represses hilA under low-osmolarity conditions. H-NS, HU, and Fis also appear to affect the derepression of hilA by HilD. Modulation of hilA by counteracting repressing and derepressing mechanisms may allow Salmonella serovar Typhimurium to regulate its virulence genes in response to different situations in vivo.
Figures

References
-
- Atlung, T., and H. Ingmer. 1997. H-NS: a modulator of environmentally regulated gene expression. Mol. Microbiol. 24:7-17. - PubMed
-
- Bajaj, V., R. L. Lucas, C. Hwang, and C. A. Lee. 1996. Co-ordinate regulation of Salmonella typhimurium invasion genes by environmental and regulatory factors is mediated by control of hilA expression. Mol. Microbiol. 22:703-714. - PubMed
-
- Caramel, A., and K. Schnetz. 1998. Lac and λ repressors relieve silencing of the Escherichia coli bgl promoter. Activation by alteration of a repressing nucleoprotein complex. J. Mol. Biol. 284:875-883. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

