TGFbeta1 signaling via alphaVbeta6 integrin
- PMID: 12935295
- PMCID: PMC184456
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-4598-2-28
TGFbeta1 signaling via alphaVbeta6 integrin
Retraction in
-
Retraction: TGFbeta1 signaling via alphaVbeta6 integrin.Mol Cancer. 2004 Jan 14;3:2. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-3-2. Mol Cancer. 2004. PMID: 14723796 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Transforming growth factor beta1 (TGFbeta1) is a potent inhibitor of epithelial cell growth, thus playing an important role in tissue homeostasis. Most carcinoma cells exhibit a reduced sensitivity for TGFbeta1 mediated growth inhibition, suggesting TGFbeta1 participation in the development of these cancers. The tumor suppressor gene DPC4/SMAD4, which is frequently inactivated in carcinoma cells, has been described as a key player in TGFbeta1 mediated growth inhibition. However, some carcinoma cells lacking functional SMAD4 are sensitive to TGFbeta1 induced growth inhibition, thus requiring a SMAD4 independent TGFbeta1 pathway.
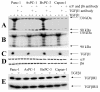
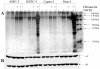
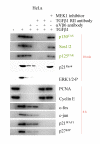
Results: Here we report that mature TGFbeta1 is a ligand for the integrin alphaVbeta6, independent of the common integrin binding sequence motif RGD. After TGFbeta1 binds to alphaVbeta6 integrin, different signaling proteins are activated in TGFbeta1-sensitive carcinoma cells, but not in cells that are insensitive to TGFbeta1. Among others, interaction of TGFbeta1 with the alphaVbeta6 integrin resulted in an upregulation of the cell cycle inhibitors p21/WAF1 and p27 leading to growth inhibition in SMAD4 deleted as well as in SMAD4 wildtype carcinoma cells.
Conclusions: Our data provide support for the existence of an alternate TGFbeta1 signaling pathway that is independent of the known SMAD pathway. This alternate pathway involves alphaVbeta6 integrin and the Ras/MAP kinase pathway and does not employ an RGD motif in TGFbeta1-sensitive tumor cells. The combined action of these two pathways seems to be necessary to elicit a complete TGFbeta1 signal.
Figures

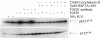




Similar articles
-
TGFbeta1 activates c-Jun and Erk1 via alphaVbeta6 integrin.Mol Cancer. 2003 Sep 23;2:33. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-2-33. Mol Cancer. 2003. Retraction in: Mol Cancer. 2004 Jan 14;3:1. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-3-1. PMID: 14572313 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Amplification of TGFβ Induced ITGB6 Gene Transcription May Promote Pulmonary Fibrosis.PLoS One. 2016 Aug 5;11(8):e0158047. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0158047. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27494713 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting endogenous transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling in SMAD4-deficient human pancreatic carcinoma cells inhibits their invasive phenotype1.Cancer Res. 2004 Aug 1;64(15):5200-11. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-0018. Cancer Res. 2004. PMID: 15289325
-
The role of integrins in TGFβ activation in the tumour stroma.Cell Tissue Res. 2016 Sep;365(3):657-73. doi: 10.1007/s00441-016-2474-y. Epub 2016 Aug 12. Cell Tissue Res. 2016. PMID: 27515461 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrin Alpha v Beta 6 (αvβ6) and Its Implications in Cancer Treatment.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 15;23(20):12346. doi: 10.3390/ijms232012346. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36293202 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Retraction: TGFbeta1 activates c-Jun and Erk1 via alphaVbeta6 integrin.Mol Cancer. 2004 Jan 14;3:1. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-3-1. Mol Cancer. 2004. PMID: 14723797 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
TGFbeta1 activates c-Jun and Erk1 via alphaVbeta6 integrin.Mol Cancer. 2003 Sep 23;2:33. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-2-33. Mol Cancer. 2003. Retraction in: Mol Cancer. 2004 Jan 14;3:1. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-3-1. PMID: 14572313 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Exploring the Role of RGD-Recognizing Integrins in Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2017 Sep 4;9(9):116. doi: 10.3390/cancers9090116. Cancers (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28869579 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Focal-adhesion-independent integrin-αv regulation of FAK and c-Myc is necessary for 3D skin formation and tumor invasion.J Cell Sci. 2015 Nov 1;128(21):3997-4013. doi: 10.1242/jcs.175539. Epub 2015 Sep 10. J Cell Sci. 2015. PMID: 26359297 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular Hsp90 and TGFβ regulate adhesion, migration and anchorage independent growth in a paired colon cancer cell line model.BMC Cancer. 2017 Mar 16;17(1):202. doi: 10.1186/s12885-017-3190-z. BMC Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28302086 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shi Y, Massague J. Mechanisms of TGF-beta signaling from cell membrane to the nucleus. Cell. 2003;113:685–700. - PubMed
-
- Massague J, Blain SW, Lo RS. TGFbeta signaling in growth control, cancer, and heritable disorders. Cell. 2000;103:295–309. - PubMed
-
- Massague J. TGFbeta signaling: receptors, transducers, and Mad proteins. Cell. 1996;85:947–950. - PubMed
-
- Massague J. Receptors for the TGF-beta family. Cell. 1992;69:1067–1070. - PubMed
-
- Cheifetz S, Weatherbee JA, Tsang ML, Anderson JK, Mole JE, Lucas R, Massague J. The transforming growth factor-beta system, a complex pattern of cross-reactive ligands and receptors. Cell. 1987;48:409–415. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

