Deciphering tuberactinomycin biosynthesis: isolation, sequencing, and annotation of the viomycin biosynthetic gene cluster
- PMID: 12936980
- PMCID: PMC182626
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.47.9.2823-2830.2003
Deciphering tuberactinomycin biosynthesis: isolation, sequencing, and annotation of the viomycin biosynthetic gene cluster
Abstract
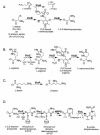
The tuberactinomycin antibiotics are essential components in the drug arsenal against Mycobacterium tuberculosis infections and are specifically used for the treatment of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis. These antibiotics are also being investigated for their targeting of the catalytic RNAs involved in viral replication and for the treatment of bacterial infections caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains and vancomycin-resistant enterococci. We report on the isolation, sequencing, and annotation of the biosynthetic gene cluster for one member of this antibiotic family, viomycin, from Streptomyces sp. strain ATCC 11861. This is the first gene cluster for a member of the tuberactinomycin family of antibiotics sequenced, and the information gained can be extrapolated to all members of this family. The gene cluster covers 36.3 kb of DNA and encodes 20 open reading frames that we propose are involved in the biosynthesis, regulation, export, and activation of viomycin, in addition to self-resistance to the antibiotic. These results enable us to predict the metabolic logic of tuberactinomycin production and begin steps toward the combinatorial biosynthesis of these antibiotics to complement existing chemical modification techniques to produce novel tuberactinomycin derivatives.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Tuberactinomycin antibiotics: Biosynthesis, anti-mycobacterial action, and mechanisms of resistance.Front Microbiol. 2022 Aug 11;13:961921. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.961921. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36033858 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification and cloning of genes encoding viomycin biosynthesis from Streptomyces vinaceus and evidence for involvement of a rare oxygenase.Gene. 2003 Jul 17;312:215-24. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1119(03)00617-6. Gene. 2003. PMID: 12909358
-
Formation of the nonproteinogenic amino acid 2S,3R-capreomycidine by VioD from the viomycin biosynthesis pathway.Chembiochem. 2004 Sep 6;5(9):1278-81. doi: 10.1002/cbic.200400187. Chembiochem. 2004. PMID: 15368581 No abstract available.
-
VioC is a non-heme iron, alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent oxygenase that catalyzes the formation of 3S-hydroxy-L-arginine during viomycin biosynthesis.Chembiochem. 2004 Sep 6;5(9):1274-7. doi: 10.1002/cbic.200400082. Chembiochem. 2004. PMID: 15368580 No abstract available.
-
Combinatorial biosynthesis of novel aminoglycoside antibiotics via pathway engineering.AMB Express. 2024 Sep 16;14(1):103. doi: 10.1186/s13568-024-01753-w. AMB Express. 2024. PMID: 39285100 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Tuberactinomycin antibiotics: Biosynthesis, anti-mycobacterial action, and mechanisms of resistance.Front Microbiol. 2022 Aug 11;13:961921. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.961921. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36033858 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Engineered Streptomyces avermitilis host for heterologous expression of biosynthetic gene cluster for secondary metabolites.ACS Synth Biol. 2013 Jul 19;2(7):384-96. doi: 10.1021/sb3001003. Epub 2013 Jan 17. ACS Synth Biol. 2013. PMID: 23654282 Free PMC article.
-
Complete sequences of conjugal helper plasmids pRK2013 and pEVS104.MicroPubl Biol. 2023 Jul 13;2023:10.17912/micropub.biology.000882. doi: 10.17912/micropub.biology.000882. eCollection 2023. MicroPubl Biol. 2023. PMID: 37521139 Free PMC article.
-
Revealing the first uridyl peptide antibiotic biosynthetic gene cluster and probing pacidamycin biosynthesis.Bioeng Bugs. 2011 Jul-Aug;2(4):218-21. doi: 10.4161/bbug.2.4.15877. Epub 2011 Jul 1. Bioeng Bugs. 2011. PMID: 21829097 Free PMC article.
-
Nonproteinogenic amino acid building blocks for nonribosomal peptide and hybrid polyketide scaffolds.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2013 Jul 8;52(28):7098-124. doi: 10.1002/anie.201208344. Epub 2013 May 31. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2013. PMID: 23729217 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alexander, F. W., E. Sandmeier, P. K. Mehta, and P. Christen. 1994. Evolutionary relationships among pyridoxal-5′-phosphate-dependent enzymes. Regio-specific alpha, beta and gamma families. Eur. J. Biochem. 219:953-960. - PubMed
-
- Battaile, K. P., J. Molin-Case, R. Paschke, M. Wang, D. Bennett, J. Vockley, and J. J. Kim. 2002. Crystal structure of rat short chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase complexed with acetoacetyl-CoA: comparison with other acyl-CoA dehydrogenases. J. Biol. Chem. 277:12200-12207. - PubMed
-
- Bibb, M. J., J. M. Ward, and S. N. Cohen. 1985. Nucleotide sequences encoding and promoting expression of three antibiotic resistance genes indigenous to Streptomyces. Mol. Gen. Genet. 199:26-36. - PubMed
-
- Bierman, M., R. Logan, K. O'Brien, E. T. Seno, R. N. Rao, and B. E. Schoner. 1992. Plasmid cloning vectors for the conjugal transfer of DNA from Escherichia coli to Streptomyces spp. Gene 116:43-49. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

