Intracellular expression of Peptide fusions for demonstration of protein essentiality in bacteria
- PMID: 12936988
- PMCID: PMC182649
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.47.9.2875-2881.2003
Intracellular expression of Peptide fusions for demonstration of protein essentiality in bacteria
Abstract
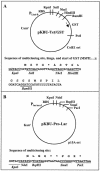
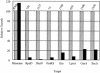
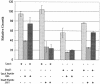
We describe a "protein knockout" technique that can be used to identify essential proteins in bacteria. This technique uses phage display to select peptides that bind specifically to purified target proteins. The peptides are expressed intracellularly and cause inhibition of growth when the protein is essential. In this study, peptides that each specifically bind to one of seven essential proteins were identified by phage display and then expressed as fusions to glutathione S-transferase in Escherichia coli. Expression of peptide fusions directed against E. coli DnaN, LpxA, RpoD, ProRS, SecA, GyrA, and Era each dramatically inhibited cell growth. Under the same conditions, a fusion with a randomized peptide sequence did not inhibit cell growth. In growth-inhibited cells, inhibition could be relieved by concurrent overexpression of the relevant target protein but not by coexpression of an irrelevant protein, indicating that growth inhibition was due to a specific interaction of the expressed peptide with its target. The protein knockout technique can be used to assess the essentiality of genes of unknown function emerging from the sequencing of microbial genomes. This technique can also be used to validate proteins as drug targets, and their corresponding peptides as screening tools, for discovery of new antimicrobial agents.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Stationary phase induction of dnaN and recF, two genes of Escherichia coli involved in DNA replication and repair.EMBO J. 1998 Mar 16;17(6):1829-37. doi: 10.1093/emboj/17.6.1829. EMBO J. 1998. PMID: 9501104 Free PMC article.
-
A novel peptide isolated from a phage display peptide library with trastuzumab can mimic antigen epitope of HER-2.J Biol Chem. 2005 Feb 11;280(6):4656-62. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M411047200. Epub 2004 Nov 9. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15536075
-
DNA knotting caused by head-on collision of transcription and replication.J Mol Biol. 2002 Sep 6;322(1):1-6. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(02)00740-4. J Mol Biol. 2002. PMID: 12215409
-
Peptide display on bacterial flagella: principles and applications.Int J Med Microbiol. 2000 Jul;290(3):223-30. doi: 10.1016/S1438-4221(00)80119-8. Int J Med Microbiol. 2000. PMID: 10959724 Review.
-
[DNA supercoiling and topoisomerases in Escherichia coli].Rev Latinoam Microbiol. 1995 Jul-Sep;37(3):291-304. Rev Latinoam Microbiol. 1995. PMID: 8850348 Review. Spanish.
Cited by
-
Structure of UDP-N-acetylglucosamine acyltransferase with a bound antibacterial pentadecapeptide.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Jul 18;103(29):10877-82. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0604465103. Epub 2006 Jul 11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16835299 Free PMC article.
-
Dual targeting antibacterial peptide inhibitor of early lipid A biosynthesis.ACS Chem Biol. 2012 Jul 20;7(7):1170-7. doi: 10.1021/cb300094a. Epub 2012 Apr 27. ACS Chem Biol. 2012. PMID: 22530734 Free PMC article.
-
Concurrent growth rate and transcript analyses reveal essential gene stringency in Escherichia coli.PLoS One. 2009 Jun 26;4(6):e6061. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0006061. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19557168 Free PMC article.
-
Structure, inhibition, and regulation of essential lipid A enzymes.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2017 Nov;1862(11):1424-1438. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2016.11.014. Epub 2016 Dec 9. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2017. PMID: 27940308 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Engineered phage-based therapeutic materials inhibit Chlamydia trachomatis intracellular infection.Biomaterials. 2012 Jul;33(20):5166-74. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2012.03.054. Epub 2012 Apr 9. Biomaterials. 2012. PMID: 22494890 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bohman, K., and L. A. Isaksson. 1980. A temperature-sensitive mutant in prolinyl-tRNA ligase of Escherichia coli K-12. Mol. Gen. Genet. 177:603-605. - PubMed
-
- Bottger, A., V. Bottger, C. Garcia-Echeverria, P. Chene, H. K. Hochkeppel, W. Sampson, K. Ang, S. F. Howard, S. M. Picksley, and D. P. Lane. 1997. Molecular characterization of the hdm2-p53 interaction. J. Mol. Biol. 269:744-756. - PubMed
-
- Bottger, V., A. Bottger, S. F. Howard, S. M. Picksley, P. Chene, C. Garcia-Echeverria, H. K. Hochkeppel, and D. P. Lane. 1996. Identification of novel mdm2 binding peptides by phage display. Oncogene 13:2141-2147. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

