Measurement of cefaclor and amoxicillin-clavulanic acid levels in middle-ear fluid in patients with acute otitis media
- PMID: 12937009
- PMCID: PMC182623
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.47.9.2987-2989.2003
Measurement of cefaclor and amoxicillin-clavulanic acid levels in middle-ear fluid in patients with acute otitis media
Abstract
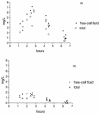
Concentrations of cefaclor (CFC) or amoxicillin-clavulanic acid (AMX/CA) in middle-ear fluid collected preserving the stability and clearing the cell contents has been compared to those obtained using the traditional method. Sixty-seven children with effusive otitis media were treated orally with CFC (20 mg/kg of body weight) or AMX/CA (20 mg/kg) (4:1 ratio). The concentrations in cell-free fluid (C-) appear higher than those in the total fluid (C+) (as assayed traditionally).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Amoxicillin-clavulanate potassium compared with cefaclor for acute otitis media in infants and children.Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1987 Mar;6(3):265-71. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198703000-00013. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1987. PMID: 3554125 Clinical Trial.
-
Multi-investigator evaluation of the efficacy and safety of cefprozil, amoxicillin-clavulanate, cefixime and cefaclor in the treatment of acute otitis media.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1994 Oct;13(10):857-65. doi: 10.1007/BF02111353. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1994. PMID: 7889960 Review.
-
A randomized controlled trial of amoxicillin plus clavulanate compared with cefaclor for treatment of acute otitis media.J Pediatr. 1986 Nov;109(5):891-6. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(86)80721-1. J Pediatr. 1986. PMID: 3534203 Clinical Trial.
-
A randomized, observer-blind trial of amoxycillin/clavulanate versus cefaclor in the treatment of children with acute otitis media. Augmentin 415 Study Group.J Chemother. 1998 Dec;10(6):460-8. doi: 10.1179/joc.1998.10.6.460. J Chemother. 1998. PMID: 9876054 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparison of cefprozil with other antibiotic regimens in the treatment of children with acute otitis media.Clin Infect Dis. 1992 Jun;14 Suppl 2:S204-8; discussion S209-11. doi: 10.1093/clinids/14.supplement_2.s204. Clin Infect Dis. 1992. PMID: 1617039 Review.
Cited by
-
New formulations of amoxicillin/clavulanic acid: a pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic review.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2005;44(11):1097-115. doi: 10.2165/00003088-200544110-00001. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2005. PMID: 16231964 Review.
-
Variations in amoxicillin pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic parameters may explain treatment failures in acute otitis media.Paediatr Drugs. 2009;11(4):243-9. doi: 10.2165/00148581-200911040-00003. Paediatr Drugs. 2009. PMID: 19566108 Review.
References
-
- Abounassif, M. A., E. M. Abdel-Moety, M. E. Mohamed, and R. A. Gad-Kariem. 1991. Liquid chromatographic determination of amoxycillin and clavulanic acid in pharmaceutical preparations. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 9: 731-735. - PubMed
-
- Chan, C. Y., K. Chan, and G. L. French. 1986. Rapid high performance liquid chromatographic assay of cefalosporins in biological fluids. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 18:537-545. - PubMed
-
- Craig, W. A. 1995. Interrelationship between pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics in determining dosage regimes for broad-spectrum cephalosporins. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 22:89-96. - PubMed
-
- Craig, W. A., and D. Andes. 1996. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of antibiotics in otitis media. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 15:944-948. - PubMed
-
- Harrison, C. J., M. I. Marks, and D. F. Welch. 1985. Microbiology of recently treated acute otitis media compared with previously untreated acute otitis media. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 4:641-646. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources