Decorin inhibition of PDGF-stimulated vascular smooth muscle cell function: potential mechanism for inhibition of intimal hyperplasia after balloon angioplasty
- PMID: 12937128
- PMCID: PMC1868258
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63447-5
Decorin inhibition of PDGF-stimulated vascular smooth muscle cell function: potential mechanism for inhibition of intimal hyperplasia after balloon angioplasty
Abstract
Decorin is a small proteoglycan that binds to transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) and inhibits its activity. However, its interaction with platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), involved in arterial repair after injury, is not well characterized. The objectives of this study were to assess decorin-PDGF and decorin-PDGF receptor (PDGFR) interactions, the in vitro effects of decorin on PDGF-stimulated smooth muscle cell (SMC) functions and the in vivo effects of decorin overexpression on arterial repair in a rabbit carotid balloon-injury model. Decorin binding to PDGF was demonstrated by solid-phase binding and affinity cross-linking assays. Decorin potently inhibited PDGF-stimulated PDGFR phosphorylation. Pretreatment of rabbit aortic SMC with decorin significantly inhibited PDGF-stimulated cell migration, proliferation, and collagen synthesis. Decorin overexpression by adenoviral-mediated gene transfection in balloon-injured carotid arteries significantly decreased intimal cross-sectional area and collagen content by approximately 50% at 10 weeks compared to beta-galactosidase-transfected or balloon-injured, non-transfected controls. This study shows that decorin binds to PDGF and inhibits its stimulatory activity on SMCs by preventing PDGFR phosphorylation. Decorin overexpression reduces intimal hyperplasia and collagen content after arterial injury. Decorin may be an effective therapy for the prevention of intimal hyperplasia after balloon angioplasty.
Figures




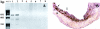
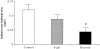

Similar articles
-
Curcumin inhibits platelet-derived growth factor-stimulated vascular smooth muscle cell function and injury-induced neointima formation.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2006 Jan;26(1):85-90. doi: 10.1161/01.ATV.0000191635.00744.b6. Epub 2005 Oct 20. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2006. PMID: 16239599
-
The cyclolignan picropodophyllin attenuates intimal hyperplasia after rat carotid balloon injury by blocking insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor signaling.J Vasc Surg. 2007 Jul;46(1):108-15. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2007.02.066. J Vasc Surg. 2007. PMID: 17606126
-
PPARγ attenuates intimal hyperplasia by inhibiting TLR4-mediated inflammation in vascular smooth muscle cells.Cardiovasc Res. 2011 Dec 1;92(3):484-93. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvr238. Epub 2011 Aug 31. Cardiovasc Res. 2011. PMID: 21880694
-
Decorin links low-density lipoproteins (LDL) to collagen: a novel mechanism for retention of LDL in the atherosclerotic plaque.Trends Cardiovasc Med. 1999 Apr-May;9(3-4):86-91. doi: 10.1016/s1050-1738(99)00013-4. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 1999. PMID: 10578523 Review.
-
Locally acting growth factors for vascular smooth muscle cells: endogenous synthesis and release from platelets.Circulation. 1985 Oct;72(4):735-40. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.72.4.735. Circulation. 1985. PMID: 3896561 Review.
Cited by
-
Extracellular matrix remodeling: the common denominator in connective tissue diseases. Possibilities for evaluation and current understanding of the matrix as more than a passive architecture, but a key player in tissue failure.Assay Drug Dev Technol. 2013 Mar;11(2):70-92. doi: 10.1089/adt.2012.474. Epub 2012 Oct 9. Assay Drug Dev Technol. 2013. PMID: 23046407 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reconstitution of marrow-derived extracellular matrix ex vivo: a robust culture system for expanding large-scale highly functional human mesenchymal stem cells.Stem Cells Dev. 2010 Jul;19(7):1095-107. doi: 10.1089/scd.2009.0217. Stem Cells Dev. 2010. PMID: 19737070 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic Disorder of Extracellular Matrix Mediated by Decorin Upregulation Is Associated With Brain Arteriovenous Malformation Diffuseness.Front Aging Neurosci. 2020 Dec 7;12:584839. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2020.584839. eCollection 2020. Front Aging Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 33364932 Free PMC article.
-
Immunomodulatory Role of the Extracellular Matrix Within the Liver Disease Microenvironment.Front Immunol. 2020 Nov 11;11:574276. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.574276. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33262757 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Decorin interferes with platelet-derived growth factor receptor signaling in experimental hepatocarcinogenesis.FEBS J. 2013 May;280(10):2150-64. doi: 10.1111/febs.12215. Epub 2013 Mar 25. FEBS J. 2013. PMID: 23448253 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schwartz R, Holmes D, Topol E: The restenosis paradigm revisited: an alternate proposal for cellular mechanisms. J Am Coll Cardiol 1992, 20:1284-1293 - PubMed
-
- Strauss BH, Chisholm RJ, Keeley FW, Gotlieb AI, Logan RA, Armstrong PW: Extracellular matrix remodeling after balloon-angioplasty injury in a rabbit model of restenosis. Circ Res 1994, 75:650-658 - PubMed
-
- Jiang B, Yamamura S, Nelson PR, Mureebe L, Kent KC: Differential effects of platelet-derived growth factor isotypes on human smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration are mediated by distinct signaling pathways. Surgery 2000, 120:427-431432 - PubMed
-
- Amento EP, Ehsani N, Palmer H, Libby P: Cytokines and growth factors positively and negatively regulate interstitial collagen gene expression in human vascular smooth muscle cells. Arterioscler Thromb 1991, 11:1223-1230 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

