Association between mitotic spindle checkpoint impairment and susceptibility to the induction of apoptosis by anti-microtubule agents in human lung cancers
- PMID: 12937152
- PMCID: PMC1868274
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63470-0
Association between mitotic spindle checkpoint impairment and susceptibility to the induction of apoptosis by anti-microtubule agents in human lung cancers
Abstract
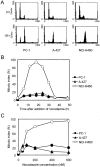
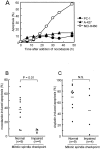
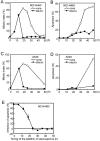
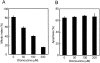
Anti-microtubule agents such as vinorelbine and paclitaxel, which are extensively used in the treatment of lung cancers, activate mitotic spindle checkpoint. Although defects of the mitotic spindle checkpoint are thought to play a role in the genesis of chromosome instability, we previously reported its frequent impairment in human lung cancer cell lines. In this study, we examined a panel of 13 human cancer cell lines comprising 11 lung and 2 other cancers and found a significant difference in the resistance to apoptosis induced by anti-microtubule agents between mitotic spindle checkpoint-impaired and -proficient cancer cell lines. This finding was in marked contrast to a lack of such correlation with a DNA damaging agent, cis-platin. Interestingly, anti-microtubule agent-induced apoptosis in mitotic spindle checkpoint-proficient cell lines, NCI-H460 and A549, was shown to be markedly reduced by staurosporine treatment in association with the shortened mitotic arrest, whereas various inhibitors of caspases seemed to have very modest effects. Taken together, these findings suggest the potential involvement of mitotic spindle checkpoint in the induction of apoptosis by anti-microtubule agents in human lung cancers, warranting further studies on the underlying mechanisms.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Requirement of a functional spindle checkpoint for arsenite-induced apoptosis.J Cell Biochem. 2008 Oct 15;105(3):678-87. doi: 10.1002/jcb.21861. J Cell Biochem. 2008. PMID: 18668508
-
Differential sensitivity of BRCA1-mutated HCC1937 human breast cancer cells to microtubule-interfering agents.Int J Oncol. 2005 May;26(5):1257-63. Int J Oncol. 2005. PMID: 15809716
-
Enhancement of paclitaxel-induced microtubule stabilization, mitotic arrest, and apoptosis by the microtubule-targeting agent EM012.Biochem Pharmacol. 2004 Dec 15;68(12):2435-41. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2004.08.032. Biochem Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 15548390
-
The effect of antimicrotubule agents on signal transduction pathways of apoptosis: a review.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1999;44(5):355-61. doi: 10.1007/s002800050989. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1999. PMID: 10501907 Review.
-
Mitotic checkpoint defects in human cancers and their implications to chemotherapy.Front Biosci. 2008 Jan 1;13:2103-14. doi: 10.2741/2827. Front Biosci. 2008. PMID: 17981695 Review.
Cited by
-
Mitosis as an anti-cancer drug target.Chromosoma. 2013 Oct;122(5):431-49. doi: 10.1007/s00412-013-0419-8. Epub 2013 Jun 18. Chromosoma. 2013. PMID: 23775312 Review.
-
Cancer drug therapy and stochastic modeling of "nano-motors".Int J Nanomedicine. 2018 Oct 15;13:6429-6440. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S168780. eCollection 2018. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018. PMID: 30410329 Free PMC article.
-
Depletion of Survivin suppresses docetaxel-induced apoptosis in HeLa cells by facilitating mitotic slippage.Sci Rep. 2021 Jan 27;11(1):2283. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-81563-3. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33504817 Free PMC article.
-
Murine leukemia P388 vinorelbine-resistant cell lines are sensitive to vinflunine.Invest New Drugs. 2008 Aug;26(4):319-30. doi: 10.1007/s10637-007-9102-3. Epub 2007 Dec 11. Invest New Drugs. 2008. PMID: 18071633
-
The ability to survive mitosis in the presence of microtubule poisons differs significantly between human nontransformed (RPE-1) and cancer (U2OS, HeLa) cells.Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 2009 Aug;66(8):437-47. doi: 10.1002/cm.20316. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 2009. PMID: 18792104 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hartwell LH, Weinert TA: Checkpoints: controls that ensure the order of cell cycle events. Science 1989, 246:629-634 - PubMed
-
- Elledge SJ: Cell cycle checkpoints: preventing an identity crisis. Science 1996, 274:1664-1672 - PubMed
-
- Takahashi T, Haruki N, Nomoto S, Masuda A, Saji S, Osada H, Takahashi T: Identification of frequent impairment of the mitotic checkpoint and molecular analysis of the mitotic checkpoint genes, hsMAD2 and p55CDC, in human lung cancers. Oncogene 1999, 18:4295-4300 - PubMed
-
- Rudner AD, Murray AW: The spindle assembly checkpoint. Curr Opin Cell Biol 1996, 8:773-780 - PubMed
-
- Lengauer C, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B: Genetic instabilities in human cancers. Nature 1998, 396:643-649 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

