The role of interleukin-4 and interleukin-12 in the progression of atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice
- PMID: 12937153
- PMCID: PMC1868277
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63471-2
The role of interleukin-4 and interleukin-12 in the progression of atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice
Abstract
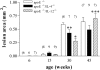
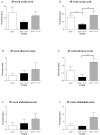
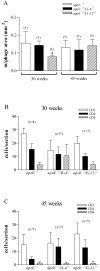
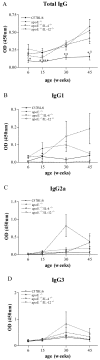
Accumulation of T cells and macrophages in atherosclerotic plaques and the formation of antibodies directed against plaque proteins suggests that adaptive immunity contributes to the development of atherosclerosis. The contribution of Th1 and Th2 helper cell subsets to atherogenesis was studied in a murine model by interbreeding apolipoprotein E-deficient (apoE(-/-)) mice with mice deficient in key cytokines that drive either Th1 responses [interleukin (IL)-12] or Th2 responses (IL-4). Compared to apoE(-/-) mice, apoE(-/-)/IL-12(-/-) mice had a 52% reduction in plaque area in the aortic root at 30 weeks of age (P < 0.001). ApoE(-/-)/IL-4(-/-) mice had a 27% reduction in plaque area compared to apoE(-/-) mice (P < 0.05) at 30 weeks of age, but their plaques were significantly larger than in apoE(-/-)/IL-12(-/-) mice at this stage (P < 0.05). By 45 weeks of age, there were no significant differences in lesion sizes in the aortic root between the strains, however apoE(-/-)/IL-4(-/-) mice showed a 58% and 64% decrease in disease in their aortic arch compared to apoE(-/-) (P < 0.05) and apoE(-/-)/IL-12(-/-) (P < 0.05) mice, respectively, and a 78% decrease in thoracic lesions compared to apoE(-/-)/IL-12(-/-) (P < 0.05). This suggests that both Th1 and Th2 cytokines play roles throughout the development of atherosclerosis in various vascular sites in apoE(-/-) mice.
Figures
References
-
- Xu QB, Oberhuber G, Gruschwitz M, Wick G: Immunology of atherosclerosis: cellular composition and major histocompatibility complex class II antigen expression in aortic intima, fatty streaks, and atherosclerotic plaques in young and aged human specimens. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 1990, 56:344-359 - PubMed
-
- Hansson GK, Jonasson L, Lojsthed B, Stemme S, Kocher O, Gabbiani G: Localization of T lymphocytes and macrophages in fibrous and complicated human atherosclerotic plaques. Atherosclerosis 1988, 72:135-141 - PubMed
-
- Van Der Wal AC, Das PK, Bentz Van De Berg D, Van Der Loos CM, Becker AE: Atherosclerotic lesions in humans: in situ immunophenotypic analysis suggesting an immune mediated response. Lab Invest 1989, 61:166-170 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

