A critical involvement of oxidative stress in acute alcohol-induced hepatic TNF-alpha production
- PMID: 12937155
- PMCID: PMC1868249
- DOI: 10.1016/s0002-9440(10)63473-6
A critical involvement of oxidative stress in acute alcohol-induced hepatic TNF-alpha production
Abstract
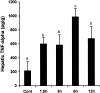
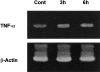
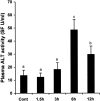
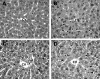
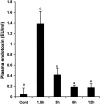
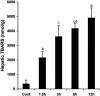
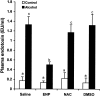
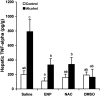
Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) production is a critical factor in the pathogenesis of alcoholic liver injury. Both oxidative stress and endotoxin have been implicated in the process of alcohol-induced TNF-alpha production. However, a cause-and-effect relationship between these factors has not been fully defined. The present study was undertaken to determine the mediators of acute alcohol-induced TNF-alpha production using a mouse model of acute alcohol hepatotoxicity. Alcohol administration via gavage at a dose of 6 g/kg to 129/Sv mice induced hepatic TNF-alpha production in Kupffer cells as demonstrated by measuring protein levels, immunohistochemical localization, and mRNA expression. Alcohol intoxication caused liver injury in association with increases in plasma endotoxin and hepatic lipid peroxidation. Treatment with an endotoxin neutralizing protein significantly suppressed alcohol-induced elevation of plasma endotoxin, hepatic lipid peroxidation, and inhibited TNF-alpha production. Treatment with antioxidants, N-ACETYL-L-CYSTEINE, or dimethylsulfoxide, failed to attenuate plasma endotoxin elevation, but significantly inhibited alcohol-induced hepatic lipid peroxidation, TNF-alpha production and steatosis. All treatments prevented alcohol-induced necrotic cell death in the liver. This study thus systemically dissected the relationship among plasma endotoxin elevation, hepatic oxidative stress, and TNF-alpha production following acute alcohol administration, and the results demonstrate that oxidative stress mediates endotoxin-induced hepatic TNF-alpha production in acute alcohol intoxication.
Figures

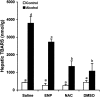
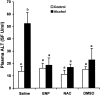
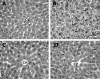
References
-
- Dufour MC, Stinson FS, Fe Case M: Trends in cirrhosis morbidity and mortality: United States, 1979–1988. Semin Liver Dis 1993, 13:109-125 - PubMed
-
- Mullen KD, Dasarathy S: Potential new therapies for alcoholic liver disease. Clin Liver Dis 1998, 2:851-881
-
- Nordmann R, Ribiere C, Rouach H: Implication of free radical mechanisms in ethanol-induced cellular injury. Free Radic Biol Med 1992, 12:219-240 - PubMed
-
- Arteel GE: Oxidants and antioxidants in alcohol-induced liver disease. Gastroenterology 2003, 124:778-790 - PubMed
-
- McClain CJ, Barve S, Deaciuc I, Kugelmas M, Hill D: Tumor necrosis factor and alcoholic liver disease. Semin Liver Dis 1999, 19:205-219 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

