Villin enhances hepatocyte growth factor-induced actin cytoskeleton remodeling in epithelial cells
- PMID: 12937273
- PMCID: PMC266779
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e03-02-0091
Villin enhances hepatocyte growth factor-induced actin cytoskeleton remodeling in epithelial cells
Abstract
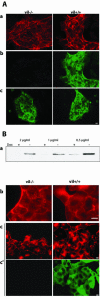
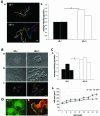
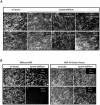
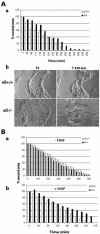
Villin is an actin-binding protein localized to intestinal and kidney brush borders. In vitro, villin has been demonstrated to bundle and sever F-actin in a calcium-dependent manner. Although villin is not necessary for the bundling of F-actin in vivo, it is important for the reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton elicited by stress during both physiological and pathological conditions (Ferrary et al., 1999). These data suggest that villin may be involved in actin cytoskeleton remodeling necessary for many processes requiring cellular plasticity. Here, we study the role of villin in hepatocyte growth factor (HGF)-induced epithelial cell motility and morphogenesis. For this purpose, we used primary cultures of enterocytes derived from wild-type and villin knock-out mice and Madin-Darby canine kidney cells, expressing villin in an inducible manner. In vitro, we show that epithelial cell lysates from villin-expressing cells induced dramatic, calcium-dependent severing of actin filaments. In cell culture, we found that villin-expressing cells exhibit enhanced cell motility and morphogenesis upon HGF stimulation. In addition, we show that the ability of villin to potentiate HGF-induced actin reorganization occurs through the HGF-activated phospholipase Cgamma signaling pathway. Collectively, these data demonstrate that villin acts as a regulator of HGF-induced actin dynamics.
Figures
References
-
- Arpin, M., Pringault, E., Finidori, J., Garcia, A., Jeltsch, J.M., Vandekerckhove, J., and Louvard, D. (1988). Sequence of human villin: a large duplicated domain homologous with other actin-severing proteins and a unique small carboxy-terminal domain related to villin specificity. J. Cell Biol. 107, 1759-1766. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Athman, R., Louvard, D., and Robine, S. (2002a). The epithelial cell cytoskeleton and intracellular trafficking. III. How is villin involved in the actin cytoskeleton dynamics in intestinal cells? Am. J. Physiol. 283, G496-G502. - PubMed
-
- Athman, R., Niewohner, J., Louvard, D., and Robine, S. (2002b). Epithelial cells: establishment of primary cultures and immortalization. In: Molecular Cellular Microbiology, vol. 31, ed. P.S.a.A. Zychlinsky, New York: Academic Press, 93-113.
-
- Bhargava, M.M., Li, Y., Joseph, A., Jin, L., Rosen, E.M., and Goldberg, I.D. (1993). HGF-SF: effects on motility and morphology of normal and tumor cells. EXS 65, 341-349. - PubMed
-
- Boyer, B., Valles, A.M., and Thiery, J.P. (1996). Model systems of epitheliummesenchyme transitions. Acta Anat. 156, 227-239. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

