Hydrogen atoms in proteins: positions and dynamics
- PMID: 12937341
- PMCID: PMC193546
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1834279100
Hydrogen atoms in proteins: positions and dynamics
Abstract
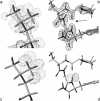
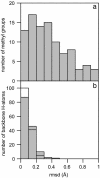
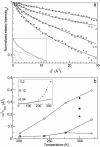
Hydrogen atoms constitute about half of the atoms in proteins. Thus they contribute to the complex energy landscape of proteins [Frauenfelder, H., Sligar, S. G. & Wolynes, P. G. (1991) Science 254, 1598-1603]. Neutron crystal structure analysis was used to study the positions and mean-square displacements of hydrogen in myoglobin. A test of the reliability of calculated hydrogen atom coordinates by a comparison with our experimental results has been carried out. The result shows that >70% of the coordinates for hydrogen atoms that have a degree of freedom is predicted worse than 0.2 A. It is shown that the mean-square displacements of the hydrogen atoms obtained from the Debye-Waller factor can be divided into three classes. A comparison with the dynamic mean-square displacements calculated from the elastic intensities obtained from incoherent neutron scattering [Doster, W., Cusack, S. & Petry, W. (1989) Nature 337, 754-756] shows that mainly the side-chain hydrogen atoms contribute to dynamic displacements on a time scale faster than 100 ps.
Figures


References
-
- Frauenfelder, H., Sligar, S. G. & Wolynes, P. G. (1991) Science 254, 1598-1603. - PubMed
-
- Kossiakoff, A. A. & Spencer, S. A. (1981) Biochemistry 20, 6462-6474. - PubMed
-
- Schmidt, M., Meier, B. & Parak, F. (1996) J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 1, 532-541.
-
- Longhi, S., Czjzek, M., Lamzin, M., Nicolas, A. & Cambillau, C. (1997) J. Mol. Biol. 268, 779-799. - PubMed
-
- Kuhn, P., Knapp, M., Soltis, S. M., Ganshaw, G., Thoene, M. & Bott, R. (1998) Biochemistry 37, 13446-13452. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

