A Comparison of Temperature Increases Produced by 2 Commonly Used Ultrasound Units
- PMID: 12937468
- PMCID: PMC155507
A Comparison of Temperature Increases Produced by 2 Commonly Used Ultrasound Units
Abstract
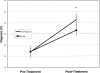
OBJECTIVE: To compare temperature changes produced by 2 commonly used ultrasound units. DESIGN AND SETTING: We inserted a thermistor microprobe connected to a digital monitor into the medial belly of the triceps surae muscle at a depth of 1.2 cm. We administered ultrasound with both the Omnisound 3000 and the Forte 400 Combo through 5-cm(2) sound heads. Continuous ultrasound was administered at a frequency of 3 MHz and an intensity of 1.0 W/cm(2). SUBJECTS: Ten (5 men, 5 women) healthy subjects (age = 21.9 +/- 0.87 years, height = 175 +/- 0.09 cm, mass = 74.2 +/- 13.3 kg) volunteered to participate in this study. MEASUREMENTS: We monitored temperature continuously during 10 minutes of ultrasound. Temperature was allowed to return to baseline between trials, and the treatment order was counterbalanced. RESULTS: We analyzed the mean temperature changes over baseline with a 2-within-factor (ultrasound unit) x 2-between-factor (sex) mixed-design analysis of variance. The mean temperature elevation was significantly greater with the Omnisound 3000 than with the Forte 400 Combo (P =.0001). Temperature increased by 5.81 +/- 0.41 degrees C with the Omnisound 3000 and only by 3.85 +/- 0.75 degrees C with the Forte 400 Combo. CONCLUSIONS: We concluded that the Omnisound 3000 was more effective in raising temperature in tissues at a depth of 1.2 cm.
Figures
References
-
- Lehmann JF, DeLateur BJ, Warren CG, Stonebridge JS. Heating produced by ultrasound in bone and soft tissue. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1967;48:397–401. - PubMed
-
- Lehmann JF, DeLateur BJ, Stonebridge JS, Warren CG. Therapeutic temperature distribution produced by ultrasound as modified by dosage and volume of tissue exposed. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1967;48:662–666. - PubMed
-
- Draper DO, Castel JC, Castel D. Rate of temperature increase in human muscle during 1 MHz and 3 MHz continuous ultrasound. J Orthop Sport Phys Ther. 1995;22:142–150. - PubMed
-
- Draper DO, Sunderland S, Kirkendall DT, Ricard M. A comparison of temperature rise in the human calf muscles following applications of underwater and topical gel ultrasound. J Orthop Sport Phys Ther. 1993;7:247–251. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources