Expression of human beta-defensins in conjunctival epithelium: relevance to dry eye disease
- PMID: 12939294
- PMCID: PMC1497873
- DOI: 10.1167/iovs.02-1301
Expression of human beta-defensins in conjunctival epithelium: relevance to dry eye disease
Abstract
Purpose: The goals of this study were to investigate whether beta-defensins are differentially expressed in the conjunctival epithelium of patients with moderate dry eye when compared with normal subjects and whether proinflammatory cytokines or bacteria can modulate the expression of human beta-defensins (hBDs)-1, -2, and -3 by conjunctival epithelial cells.
Methods: RNA extracted from conjunctival impression cytology specimens of eight normal subjects and nine patients with moderate dry eye was used in RT-PCR to detect mRNA for hBDs-1, -2, and -3. Two conjunctival epithelial cell lines and primary cultured conjunctival epithelial cells were treated with proinflammatory cytokines or heat-killed Pseudomonas aeruginosa. RT-PCR and immunoblot analysis were used to detect mRNA for hBD-1, -2, and -3 and protein secretion of hBD-2, respectively.
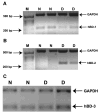
Results: hBD-2 message was detected in RNA samples of eight of nine patients with dry eye, but not in any of the normal subjects' samples, whereas hBD-1 and -3 were detected in all subjects tested. RT-PCR revealed an upregulation of hBD-2 but no difference in expression of hBD-1 and -3 in cultured conjunctival cells after a 24-hour treatment with 10 ng/mL interleukin (IL)-1beta, IL-1beta and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (10 ng/mL) or heat-killed Pseudomonas aeruginosa (1 million colony-forming units; n = 3). hBD-2 expression was upregulated from 4 hours of treatment with IL-1beta (at 10 ng/mL; (n = 2-3) and at a concentration of 0.1 ng/mL IL-1beta (24-hour treatment; n = 2-3). Immunoblots demonstrated protein secretion results corresponding to the RT-PCR data.
Conclusions: hBD-2 was expressed only in the conjunctival epithelium of patients with moderate dry eye. Because cytokines such as IL-1beta and TNF-alpha induced the expression of hBD-2 by conjunctival epithelial cells and because increased proinflammatory cytokine activity is a feature of dry eye disease, it can be speculated that the hBD-2 upregulation observed in subjects with moderate dry eye is mediated by proinflammatory cytokine activity.
Figures



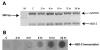
Similar articles
-
Defensin expression by the cornea: multiple signalling pathways mediate IL-1beta stimulation of hBD-2 expression by human corneal epithelial cells.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2003 May;44(5):1859-65. doi: 10.1167/iovs.02-0787. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2003. PMID: 12714616 Free PMC article.
-
Conjunctival cytokine expression in symptomatic moderate dry eye subjects.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2006 Jun;47(6):2445-50. doi: 10.1167/iovs.05-1364. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2006. PMID: 16723455
-
Toll-like receptor activation modulates antimicrobial peptide expression by ocular surface cells.Exp Eye Res. 2011 Mar;92(3):209-20. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2010.12.005. Epub 2010 Dec 31. Exp Eye Res. 2011. PMID: 21195713 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-1β and tumour necrosis factor-α levels in conjunctiva of diabetic patients with symptomatic moderate dry eye: case-control study.BMJ Open. 2016 Aug 3;6(8):e010979. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2015-010979. BMJ Open. 2016. PMID: 27489152 Free PMC article.
-
Cationic amino acid transporters and beta-defensins in dry eye syndrome.Dev Ophthalmol. 2010;45:12-15. doi: 10.1159/000315015. Epub 2010 May 18. Dev Ophthalmol. 2010. PMID: 20502022 Review.
Cited by
-
TLRs and NODs mRNA expression pattern in healthy mouse eye.Br J Ophthalmol. 2005 Jul;89(7):904-10. doi: 10.1136/bjo.2004.056218. Br J Ophthalmol. 2005. PMID: 15965176 Free PMC article.
-
Conjunctival impression cytology versus routine tear function tests for dry eye evaluation in contact lens wearers.J Cytol. 2015 Oct-Dec;32(4):261-7. doi: 10.4103/0970-9371.171242. J Cytol. 2015. PMID: 26811575 Free PMC article.
-
An Overview of Frog Skin-Derived Esc Peptides: Promising Multifunctional Weapons against Pseudomonas aeruginosa-Induced Pulmonary and Ocular Surface Infections.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 16;25(8):4400. doi: 10.3390/ijms25084400. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38673985 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In vitro activity of human beta-defensin 2 against Pseudomonas aeruginosa in the presence of tear fluid.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007 Nov;51(11):3853-60. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01317-06. Epub 2007 Aug 27. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007. PMID: 17724155 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro studies on the antimicrobial peptide human beta-defensin 9 (HBD9): signalling pathways and pathogen-related response (an American Ophthalmological Society thesis).Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc. 2014 Jul;112:50-73. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc. 2014. PMID: 25646028 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lemp MA. Report of the National Eye Institute/Industry workshop on Clinical Trials in Dry Eyes. CLAO J. 1995;21:221–232. - PubMed
-
- Stern ME, Beuerman RW, Fox RI, et al. The pathology of dry eye: the interaction between the ocular surface and lacrimal glands. Cornea. 1998;17:584–589. - PubMed
-
- Pflugfelder SC. Differential diagnosis of dry eye conditions. Adv Dent Res. 1996;10:9–12. - PubMed
-
- Pflugfelder SC, Jones D, Ji Z, Afonso A, Monroy D. Altered cytokine balance in the tear fluid and conjunctiva of patients with Sjogren’s syndrome keratoconjunctivitis sicca. Curr Eye Res. 1999;19:201–211. - PubMed
-
- Solomon A, Dursun D, Liu Z, et al. Pro- and anti-inflammatory forms of interleukin-1 in the tear fluid and conjunctiva of patients with dry-eye disease. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2001;42:2283–2292. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

