Inhibition of DC-SIGN-mediated trans infection of T cells by mannose-binding lectin
- PMID: 12941144
- PMCID: PMC1783022
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2567.2003.01707.x
Inhibition of DC-SIGN-mediated trans infection of T cells by mannose-binding lectin
Abstract
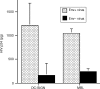
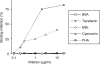
Some dendritic cells (DC) express a cell-surface lectin called 'dendritic cell-specific intracellular adhesion molecule 3 (ICAM-3)-grabbing non-integrin' (DC-SIGN). DC-SIGN has been shown to mediate a type of infection called 'trans' infection, where DC bind human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and efficiently transfer the virus to T cells. We investigated the possibility that mannose-binding lectin (MBL), a soluble lectin that functions as a recognition molecule in innate immunity and that binds to HIV, could block trans infection mediated by DC-SIGN. Binding studies with glycoprotein (gp)120/gp41-positive and -negative virus preparations suggested that DC-SIGN and MBL bind primarily to glycans on gp120/gp41, as opposed to glycans on host-cell-derived proteins, indicating a close overlap in the binding site of the two lectins and supporting the notion that MBL could prevent binding of HIV to DC-SIGN. Preincubation of X4, R5 or dual-tropic HIV strains with MBL prevented DC-SIGN-mediated trans infection of T cells. The mechanism of MBL blocking trans infection of T cells was at least partly caused by blocking of virus binding to DC-SIGN positive cells. This study shows that MBL prevents DC-SIGN-mediated trans infection of T cells in vitro and suggests that in infected persons, MBL may inhibit DC-SIGN-mediated uptake and spread of HIV.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Mannose-binding lectin binds to Ebola and Marburg envelope glycoproteins, resulting in blocking of virus interaction with DC-SIGN and complement-mediated virus neutralization.J Gen Virol. 2005 Sep;86(Pt 9):2535-2542. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.81199-0. J Gen Virol. 2005. PMID: 16099912
-
High doses of recombinant mannan-binding lectin inhibit the binding of influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 virus with cells expressing DC-SIGN.APMIS. 2017 Jul;125(7):655-664. doi: 10.1111/apm.12695. Epub 2017 May 11. APMIS. 2017. PMID: 28493491
-
Colorectal mucus binds DC-SIGN and inhibits HIV-1 trans-infection of CD4+ T-lymphocytes.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 20;10(3):e0122020. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0122020. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25793526 Free PMC article.
-
DC-SIGN (dendritic cell-specific ICAM-grabbing non-integrin) and DC-SIGN-related (DC-SIGNR): friend or foe?Clin Sci (Lond). 2003 Apr;104(4):437-46. Clin Sci (Lond). 2003. PMID: 12653690 Review.
-
Mannose binding lectin (MBL) and HIV.Mol Immunol. 2005 Feb;42(2):145-52. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2004.06.015. Mol Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15488604 Review.
Cited by
-
Functional contributions of carbohydrate on AIDS virus glycoprotein.Yale J Biol Med. 2010 Dec;83(4):201-8. Yale J Biol Med. 2010. PMID: 21165339 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mannose-binding lectin in HIV infection.Future Virol. 2008 May;3(3):225-233. doi: 10.2217/17460794.3.3.225. Future Virol. 2008. PMID: 21218140 Free PMC article.
-
Protein-Protein Interaction between Surfactant Protein D and DC-SIGN via C-Type Lectin Domain Can Suppress HIV-1 Transfer.Front Immunol. 2017 Jul 31;8:834. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00834. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28824609 Free PMC article.
-
A neuron-specific antiviral mechanism prevents lethal flaviviral infection of mosquitoes.PLoS Pathog. 2015 Apr 27;11(4):e1004848. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004848. eCollection 2015 Apr. PLoS Pathog. 2015. PMID: 25915054 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Lectins from Metastatic Cancer Cells through Magnetic Glyconanoparticles.Isr J Chem. 2015 Mar 1;55(3-4):423-436. doi: 10.1002/ijch.201400156. Epub 2015 Mar 23. Isr J Chem. 2015. PMID: 27110035 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Geijtenbeek TB, Krooshoop DJ, Bleijs DA, et al. DC-SIGN–ICAM−2 interaction mediates dendritic cell trafficking. Nat Immunol. 2000;1:353. - PubMed
-
- Geijtenbeek TB, Torensma R, van Vliet SJ, van Duijnhoven GC, Adema GJ, van Kooyk Y, Figdor CG. Identification of DC-SIGN, a novel dendritic cell-specific ICAM-3 receptor that supports primary immune responses. Cell. 2000;100:575. - PubMed
-
- Figdor CG, van Kooyk Y, Adema GJ. C-type lectin receptors on dendritic cells and Langerhans' cells. Nat Rev Immunol. 2002;2:77. - PubMed
-
- Geijtenbeek TB, Kwon DS, Torensma R, et al. DC-SIGN, a dendritic cell-specific HIV-1-binding protein that enhances trans-infection of T cells. Cell. 2000;100:587. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

