Binding, activation and dissociation of the dimeric SecA ATPase at the dimeric SecYEG translocase
- PMID: 12941690
- PMCID: PMC202361
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/cdg418
Binding, activation and dissociation of the dimeric SecA ATPase at the dimeric SecYEG translocase
Abstract
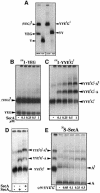
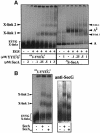
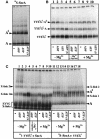
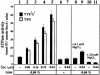
The bacterial preprotein translocase is comprised of a membrane-embedded oligomeric SecYEG structure and a cytosolic dimeric SecA ATPase. The associations within SecYEG oligomers and SecA dimers, as well as between these two domains are dynamic and reversible. Here, it is shown that a covalently linked SecYEG dimer forms a functional translocase and a high affinity binding site for monomeric and dimeric SecA in solution. The interaction between these two domains stimulates the SecA ATPase, and nucleotides modulate the affinity and ratio of SecA monomers and dimers bound to the linked SecYEG complex. During the translocation reaction, the SecA monomer remains in stable association with a SecYEG protomer and the translocating preprotein. The nucleotides and translocation-dependent changes of SecA-SecYEG associations and the SecA dimeric state may reflect important facets of the preprotein translocation reaction.
Figures


References
-
- Benach J. et al. (2003) Phospholipid-induced monomerization and signal-peptide-induced oligomerization of SecA. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 3628–3638. - PubMed
-
- Breukink E., Nouwen,N., van Raalte,A., Mizushima,S., Tommassen,J. and de Kruijff,B. (1995) The C terminus of SecA is involved in both lipid binding and SecB binding. J. Biol. Chem., 270, 7902–7907. - PubMed
-
- Breyton C., Haase,W., Rapoport,T.A., Kuhlbrandt,W. and Collinson,I. (2002) Three-dimensional structure of the bacterial protein-translocation complex SecYEG. Nature, 418, 662–665. - PubMed
-
- Cao T.B. and Saier,M.H. (2003) The general protein secretory pathway: phylogenetic analyses leading to evolutionary conclusions. Biochim. Biophys Acta, 1609, 115–125. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

