A role for MEK kinase 1 in TGF-beta/activin-induced epithelium movement and embryonic eyelid closure
- PMID: 12941696
- PMCID: PMC202382
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/cdg440
A role for MEK kinase 1 in TGF-beta/activin-induced epithelium movement and embryonic eyelid closure
Abstract
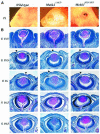
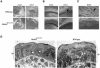
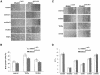
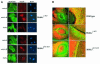
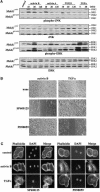
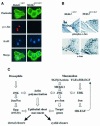
MEKK1-deficient mice show an eye open at birth phenotype caused by impairment in embryonic eyelid closure. MEK kinase 1 (MEKK1) is highly expressed in the growing tip of the eyelid epithelium, which displays loose cell-cell contacts and prominent F-actin fibers in wild-type mice, but compact cell contacts, lack of polymerized actin and a concomitant impairment in c-Jun N-terminal phosphorylation in MEKK1-deficient mice. In cultured keratinocytes, MEKK1 is essential for JNK activation by TGF-beta and activin, but not by TGF-alpha. MEKK1-driven JNK activation is required for actin stress fiber formation, c-Jun phosphorylation and cell migration. However, MEKK1 ablation does not impair other TGF-beta/activin functions, such as nuclear translocation of Smad4. These results establish a specific role for the MEKK1-JNK cascade in transmission of TGF-beta and activin signals that control epithelial cell movement, providing the mechanistic basis for the regulation of eyelid closure by MEKK1. This study also suggests that the signaling mechanisms that control eyelid closure in mammals and dorsal closure in Drosophila are evolutionarily conserved.
Figures

References
-
- Ashrafi S.H., Atassi,B., Erickson,R. and Sabet,T. (1993) Migration of epithelium during phenytoin-dependent gingival overgrowth in mice. Scanning Microsc., 7, 1247–1253. - PubMed
-
- Bakin A.V., Tomlinson,A.K., Bhowmick,N.A., Moses,H.L. and Arteaga,C.L. (2000) Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase function is required for transforming growth factor beta-mediated epithelial to mesenchymal transition and cell migration. J. Biol. Chem., 275, 36803–36810. - PubMed
-
- Berkowitz E.A. et al. (1996) Characterization of the mouse transforming growth factor alpha gene: its expression during eyelid development and in waved 1 tissues. Cell Growth Differ., 7, 1271–1282. - PubMed
-
- Birk D.E. and Mayne,R. (1997) Localization of collagen types I, III and V during tendon development. Changes in collagen types I and III are correlated with changes in fibril diameter. Eur. J. Cell Biol., 72, 352–361. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

