HS5 of the human beta-globin locus control region: a developmental stage-specific border in erythroid cells
- PMID: 12941700
- PMCID: PMC202379
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/cdg437
HS5 of the human beta-globin locus control region: a developmental stage-specific border in erythroid cells
Abstract
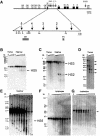
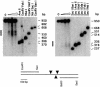
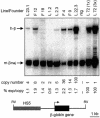
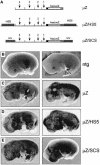
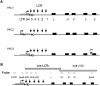
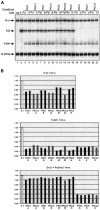
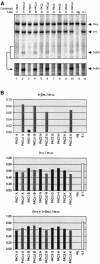
Elements with insulator/border activity have been characterized most extensively in Drosophila melanogaster. In vertebrates, the first example of such an element was provided by a hypersensitive site of the chicken beta-globin locus, cHS4. It has been proposed that the homologous site in humans, HS5, functions as a border of the human beta-globin locus. Here, we have characterized HS5 of the human beta-globin locus control region. We have examined its tissue-specificity and assessed its insulating properties in transgenic mice using a lacZ reporter assay. Most importantly, we have tested its enhancer blocking activity in the context of the full beta-globin locus. Our results show that HS5 is erythroid-specific rather than ubiquitous in human tissues. Furthermore, HS5 does not fulfil the criteria of a general in vivo insulator in the transgene protection assay. Finally, a HS5 conditional deletion from the complete locus demonstrates that HS5 has no discernable activity in adult erythroid cells. Surprisingly, HS5 functions as an enhancer blocker in embryonic erythroid cells. We conclude that HS5 is a developmental stage-specific border in erythroid cells.
Figures
References
-
- Antoniou M. (1991) Induction of erythroid-specific expression in murine erythroleukemia (MEL) cell lines. Methods Mol. Biol., 7, 421–434. - PubMed
-
- Bender M.A., Bulger,M., Close,J. and Groudine,M. (2000) β-globin gene switching and DNase I sensitivity of the endogenous β-globin locus in mice do not require the locus control region. Mol. Cell, 5, 387–393. - PubMed
-
- Carter D., Chakalova,L., Osborne,C.S., Dai,Y.F. and Fraser,P. (2002) Long-range chromatin regulatory interactions in vivo. Nat. Genet., 32, 623–626. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

