The cap region of topoisomerase I binds to sites near both ends of simian virus 40 T antigen
- PMID: 12941889
- PMCID: PMC224608
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.77.18.9809-9816.2003
The cap region of topoisomerase I binds to sites near both ends of simian virus 40 T antigen
Abstract
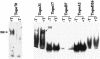
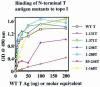
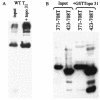
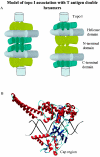
Two independent binding sites on simian virus 40 (SV40) T antigen for topoisomerase I (topo I) were identified. One was mapped to the N-terminal domain (residues 83 to 160) by a combination of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs) and glutathione S-transferase (GST) pull-down assays performed with various T antigen deletion mutants. The second was mapped to the C-terminal domain (residues 602 to 708). The region in human topo I that binds to both sites in T antigen was identified by ELISAs, GST pull-down assays, and double-hexamer binding assays with topo I deletion mutants. This region corresponds to a distinct domain on topo I known as the cap region that maps from residues 175 to 433. By combining these data with information about the structure of T-antigen double hexamers associated with origin DNA, we propose that the cap region of topo I associates specifically with both ends of the double hexamer bound to the SV40 origin to initiate DNA replication.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Simian virus 40 DNA replication is dependent on an interaction between topoisomerase I and the C-terminal end of T antigen.J Virol. 2008 Feb;82(3):1136-45. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01314-07. Epub 2007 Nov 14. J Virol. 2008. PMID: 18003733 Free PMC article.
-
Simian virus 40 large T antigen binds to topoisomerase I.Virology. 1996 Aug 15;222(2):365-74. doi: 10.1006/viro.1996.0433. Virology. 1996. PMID: 8806520
-
Topoisomerase I associates specifically with simian virus 40 large-T-antigen double hexamer-origin complexes.J Virol. 2000 Jun;74(11):5224-32. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.11.5224-5232.2000. J Virol. 2000. PMID: 10799598 Free PMC article.
-
The role of the J domain of SV40 large T in cellular transformation.Biologicals. 1999 Mar;27(1):23-8. doi: 10.1006/biol.1998.0173. Biologicals. 1999. PMID: 10441399 Review.
-
Interactions between DNA replication-related proteins and phospholipid vesicles in vitro.Chem Phys Lipids. 1994 Sep 6;73(1-2):223-30. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(94)90183-x. Chem Phys Lipids. 1994. PMID: 8001183 Review.
Cited by
-
Timed interactions between viral and cellular replication factors during the initiation of SV40 in vitro DNA replication.Biochem J. 2007 Oct 15;407(2):313-20. doi: 10.1042/BJ20070794. Biochem J. 2007. PMID: 17666013 Free PMC article.
-
Validation of BKV large T-antigen ATP-binding site as a target for drug discovery.Antiviral Res. 2009 Feb;81(2):184-7. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2008.11.004. Epub 2008 Dec 11. Antiviral Res. 2009. PMID: 19084558 Free PMC article.
-
Biologic diversity of polyomavirus BK genomic sequences: Implications for molecular diagnostic laboratories.J Med Virol. 2008 Oct;80(10):1850-7. doi: 10.1002/jmv.21281. J Med Virol. 2008. PMID: 18712842 Free PMC article.
-
DNA damage-induced phosphorylation of a replicative DNA helicase results in inhibition of DNA replication through attenuation of helicase function.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Sep 23;52(17):10311-10328. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae663. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 39126317 Free PMC article.
-
Assembly of the replication initiation complex on SV40 origin DNA.Nucleic Acids Res. 2004 Feb 11;32(3):1103-12. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkh236. Print 2004. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004. PMID: 14960720 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Borowiec, J. A., F. B. Dean, P. A. Bullock, and J. Hurwitz. 1990. Binding and unwinding: how T antigen engages the SV40 origin of DNA replication. Cell 60:181-184. - PubMed
-
- Braun, K. A., Y. Lao, Z. He, C. J. Ingles, and M. S. Wold. 1997. Role of protein-protein interactions in the function of replication protein A (RPA): RPA modulates the activity of DNA polymerase alpha by multiple mechanisms. Biochemistry 36:8443-8454. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

