Integrin-using rotaviruses bind alpha2beta1 integrin alpha2 I domain via VP4 DGE sequence and recognize alphaXbeta2 and alphaVbeta3 by using VP7 during cell entry
- PMID: 12941907
- PMCID: PMC224597
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.77.18.9969-9978.2003
Integrin-using rotaviruses bind alpha2beta1 integrin alpha2 I domain via VP4 DGE sequence and recognize alphaXbeta2 and alphaVbeta3 by using VP7 during cell entry
Abstract
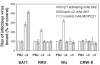
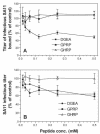
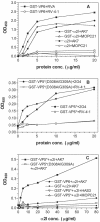
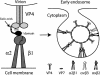
Integrins alpha2beta1, alphaXbeta2, and alphaVbeta3 have been implicated in rotavirus cell attachment and entry. The virus spike protein VP4 contains the alpha2beta1 ligand sequence DGE at amino acid positions 308 to 310, and the outer capsid protein VP7 contains the alphaXbeta2 ligand sequence GPR. To determine the viral proteins and sequences involved and to define the roles of alpha2beta1, alphaXbeta2, and alphaVbeta3, we analyzed the ability of rotaviruses and their reassortants to use these integrins for cell binding and infection and the effect of peptides DGEA and GPRP on these events. Many laboratory-adapted human, monkey, and bovine viruses used integrins, whereas all porcine viruses were integrin independent. The integrin-using rotavirus strains each interacted with all three integrins. Integrin usage related to VP4 serotype independently of sialic acid usage. Analysis of rotavirus reassortants and assays of virus binding and infectivity in integrin-transfected cells showed that VP4 bound alpha2beta1, and VP7 interacted with alphaXbeta2 and alphaVbeta3 at a postbinding stage. DGEA inhibited rotavirus binding to alpha2beta1 and infectivity, whereas GPRP binding to alphaXbeta2 inhibited infectivity but not binding. The truncated VP5* subunit of VP4, expressed as a glutathione S-transferase fusion protein, bound the expressed alpha2 I domain. Alanine mutagenesis of D308 and G309 in VP5* eliminated VP5* binding to the alpha2 I domain. In a novel process, integrin-using viruses bind the alpha2 I domain of alpha2beta1 via DGE in VP4 and interact with alphaXbeta2 (via GPR) and alphaVbeta3 by using VP7 to facilitate cell entry and infection.
Figures

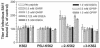

References
-
- Barton, E. S., J. C. Forrest, J. L. Connolly, J. D. Chappell, Y. Liu, F. J. Schnell, A. Nusrat, C. A. Parkos, and T. S. Dermody. 2001. Junction adhesion molecule is a receptor for reovirus. Cell 104:441-451. - PubMed
-
- Bergelson, J. M., N. F. St. John, S. Kawaguchi, R. Pasqualini, F. Berdichevsky, M. E. Hemler, and R. W. Finberg. 1994. The I domain is essential for echovirus 1 interaction with VLA-2. Cell Adhes. Commun. 2:455-464. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

