Analysis of early human immunodeficiency virus type 1 DNA synthesis by use of a new sensitive assay for quantifying integrated provirus
- PMID: 12941923
- PMCID: PMC224570
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.77.18.10119-10124.2003
Analysis of early human immunodeficiency virus type 1 DNA synthesis by use of a new sensitive assay for quantifying integrated provirus
Abstract
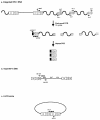
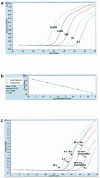
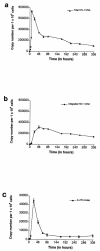
A novel Alu-long terminal repeat (LTR)-based real-time nested-PCR assay was developed to quantify integrated human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) DNA in infected cells with both accuracy and high sensitivity (six proviruses within 50,000 cell equivalents). Parallel assays for total HIV-1 DNA and two-LTR HIV-1 DNA circles allowed the synthesis and fate of the different HIV-1 DNA species to be monitored upon a single round of viral replication.
Figures
References
-
- Barbosa, P., P. Charneau, N. Dumey, and F. Clavel. 1994. Kinetic analysis of HIV-1 early replicative steps in a coculture system. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 10:53-59. - PubMed
-
- Brussel, A., D. Mathez, S. Broche-Pierre, R. Lancar, T. Calvez, P. Sonigo, and J. Leibowitch. 2003. Longitudinal monitoring of 2-long terminal repeat circles in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with chronic HIV-1 infection. AIDS 17:645-652. - PubMed
-
- Butler, S. L., M. S. Hansen, and F. D. Bushman. 2001. A quantitative assay for HIV DNA integration in vivo. Nat. Med. 7:631-634. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

